

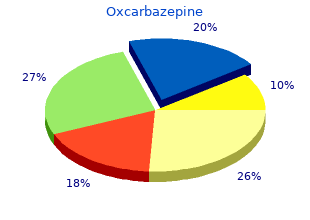
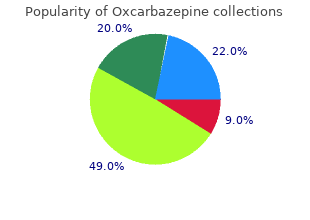
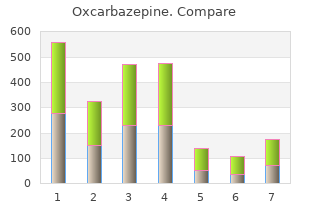
Grinnell College. F. Asaru, MD: "Order Oxcarbazepine online - Proven Oxcarbazepine OTC".
This is important order oxcarbazepine 150mg line symptoms anxiety, for it avoids genital herpes the incorrect diagnosis of genital herpes in women Acyclovir 400 mg orally three times a day for who remain antibody negative buy oxcarbazepine cheap medications side effects prescription drugs. This indicates a Acyclovir 200 mg orally fve times a day for primary infection purchase oxcarbazepine 600mg visa symptoms schizophrenia, and different advice should be 7–10 days given depending upon the herpes isolate. They should 7–10 days be alerted to inform the physician if they have any or symptoms suggestive of a recurrence so they can Famciclovir 250 mg orally three times a day for be reevaluated. The patient should be advised to keep a Vulvovaginal Infections 84 calendar to document the frequency of recurrences so that judgments can be made about either inter- Table 8. They regimens for episodic genital herpes should also have a prescription for antiviral medi- infections cation so that it can be taken if they have prodro- Acyclovir 400 mg orally three times a day for mal symptoms. These women have many questions 5 days that the physician needs to address as accurately or as possible. Is their most recent sexual partner the Acyclovir 800 mg orally twice a day for 5 days source of the infection? These partners could be or asymptomatic shedders of the virus but unaware Acyclovir 800 mg orally twice a day for 2 days that they have genital herpes. Contracting genital herpes is a medical event that has terminated many or relationships. Sexually active women, not currently Valacyclovir 500 mg orally twice a day for 3 days in a monogamous relationship, have an impor- or tant question. The risk is greater Famciclovir 125 mg orally twice a day for 5 days when they have vulvar lesions, but these patients or can also have asymptomatic shedding of the virus. These women can be advised to inform any poten- tial sexual partners that they have genital herpes. If susceptible, there are antiviral agent on hand so that they are not scurry- options to reduce the risk. Obviously, the couple ing at night or on the weekend searching for a doc- should avoid any intimate contact when there are tor on call to obtain a prescription and then have to either prodromal symptoms or any genital lesions fnd an open pharmacy to obtain these drugs. In addition, placing the woman on once is a wide range of treatment regimens available35 daily valacyclovir reduces, but does not eliminate, (Table 8. This dis- is whether or not, should they get pregnant, they rupts their work and social lives, and an appropriate can give birth to a healthy, noninfected newborn. They should be counseled that such will be monitored and that if they have a genital medication will reduce the number of outbreaks but outbreak when they go into labor, a cesarean sec- may not prevent all of them. They also these women, the frequency of outbreaks will deter- should be aware that susceptible men are at lower risk mine the future therapeutic strategy. In In the patient diagnosed with genital herpes, one study comparing the use of valacyclovir 500 mg the strategy of how to deal with recurrent episodes once a day to placebo in which condoms were used should be in place before the next episode occurs. In addi- effective than either valacyclovir or acyclovir tion, this is one population of patients in which the dosing regimens in persons who have very fre- possibility of the development of resistance by her- quent recurrences (i. Signifcance was achieved when the data on Fortunately, this is an uncommon event, estimated susceptible females were combined with that of sus- to be 1 in 3,200 deliveries in the United States10 ceptible males. These immuno- pling would be avoided in the event that they were compromised women can have severe episodes of asymptomatically shedding the virus at the time of genital herpes that often are prolonged and painful. If there are frequent sive antiviral therapy for the last 4 weeks of gesta- recurrences, these women should be candidates for tion. The treatment of genital herpes is shown to lower the numbers of newborn infections an important frst step but must be accompanied due to herpes. If they 5–10 days are, they should be instructed to recognize these reactivations and alert the physicians if they occur Vulvovaginal Infections 86 just prior to or at the onset of labor. A primary mater- Herpes, an incurable virus, threatens to undo nal infection with either virus in the third trimester the sexual revolution. Herpes simplex virus type 2 in the not yet been established, and the question of cost- United States, 1976 to 1994. N Engl J Med effectiveness in view of the infrequency of genital 1997;337:1105–1111. To decrease this risk, genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infection barring sexual abstinence, the male can either use in asymptomatic seropositive persons. Recurrence infection in a pregnant woman carries a higher rates in genital herpes after symptomatic risk of transmission to the newborn than a pri- frst-episode infection. Herpes simplex virus infection as a risk factor for human immunodefciency provide added protection. Animal trials of this drug have been States among asymptomatic women unaware of promising, for they have lowered the frequency of any herpes simplex virus infection (Herpevac virus shedding. Overlapping reactivations of herpes sim- Herpes simplex virus type 2 detection by plex virus type 2 in the genital and perianal culture and polymerase chain reaction and mucosa. An appraisal of screen- tion increases the risk of subsequent epi- ing for maternal type-specifc herpes simplex sodes of bacterial vaginosis. Neonatal herpes sim- Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin plex infection in the British Isles. Paediatr concentration in vaginal fuid: Relation to bac- Perinat Epidemiol 1996;10:432–442. Once daily ery on transmission of herpes simplex virus valacyclovir to reduce the risk of trans- from mother to infant. J Am Med Assoc herpes simplex virus shedding and cesarean deliv- 1999;282:331–340. A case for wider adaptive immunity against herpes simplex herpes simplex virus serologic testing. Glycoprotein d-adjuvant vaccine the genital mucosa: Insights into the mucosal to prevent genital herpes. Male circumcision and herpes simplex virus Antiviral activity of trappin-2 and elafn type 2 infections in female partners: A ran- in vitro and in vivo against genital herpes. They have been will cause these women to overwhelm private physi- labeled “low risk” because they are not associated cian offces with phone calls seeking assurances that with cancers of the cervix, vagina, vulva, or rectum. Anyone testing asymptomatic women Annual Pap smear screening is no longer con- will fnd many more patients with a positive low-risk sidered the standard of care in the United States. If the Pap smear is absence of any clinical abnormalities will require an normal, then repeated Pap smears can be done at explanation and a follow-up plan. Equally damaging, these lesions con- England, for example, the frst Pap smear is not rec- frm that her partner was indiscreet in a relationship ommended until the age of 25. The unexpected tioners must be prepared to modify these guidelines appearance of genital warts in the trusting female if uncommon individual patient circumstances sug- of a married couple is frequently the frst step on gest alterations. Very reaction of most women to this new physical reality early sexual exposure could lead to invasive cervical is to seek immediate treatment to rid themselves of Vulvovaginal Infections 90 these lesions. They also want to be assured that con- study of poor urban women in Sao Paulo, Brazil, dyloma removal will end their concerns about trans- had similar fndings. They feel violated and unclean, and they want the physician, the clinical reality is a large popula- immediate treatment to eliminate these growths.
Usage: ut dict.
Transcervico-mandibulo- palatal approach for surgical salvage of recurrent nasopharyngeal cancer order genuine oxcarbazepine line medicine balls for sale. Laryngoscope 2006 buy oxcarbazepine 300 mg visa symptoms your having a boy;116(5):839–841 Anatomy of the Sphenoid and 18 Adjacent Structures of Importance during Skull Base Surgery When the sphenoid sinus is opened and entered with an Anatomy of the Pituitary Fossa endoscope the surgeon should be able to identify whether the dominant sinus is entered buy cheap oxcarbazepine 150mg on line medicine bottle. If the intersinus septum Bone is removed from cavernous sinus to cavernous sinus, attaches to the lateral wall of the sphenoid, usually in the onto the foor of the fossa and up to the tuberculum sella. Once the bone front of the surgeon and the pituitary fossa is not seen, the over the pituitary fossa has been removed, the underly- surgeon should be in the nondominant sinus. This space is occupied by ve- Once the intersinus septum is removed (usually with a nous channels that connect the cavernous sinuses in the through-biting Blakesley or diamond burr—twisting should upper and lower regions of the pituitary (Fig. In be avoided to avoid possible damage to the carotid artery most macroadenomas these venous channels are obliter- by fracturing bone), the normal structures should be iden- ated by the pressure from the enlarging tumor. The pituitary fossa is seen in the midline with the in microadenomas and tuberculum sella meningiomas, anterior genu of the cavernous carotid seen on either side. Bipolar cautery may seal the channels but are seen at the junction of the side wall and roof. There is often the most efective way is to open the dura and then often a depression between the optic nerve and carotid in attempt to seal the two layers with bipolar cautery. This is injected into the region and pressure is optic nerve at the point where it leaves the sphenoid and applied with a neuropattie. On the lateral wall the V2 branch of the trigeminal nerve can be seen as well as the vidian nerve in the foor of the sinus. Depending on the sphenoid pneumatization Lateral Wall of the Pituitary Fossa this bone may be either thick or quite thin. On either side of the clivus are the vertical paraclival portions of the carotid The lateral wall of the pituitary fossa is formed by the cavern- (Fig. These are important landmarks for any surgical ous sinus and the cavernous portion of the carotid artery. Tumor is routinely thickened area of bone that forms the junction between the removed from the lateral wall with suction and standard anterior face of the pituitary fossa and the roof of the sphe- pituitary curettes so knowing where to expect the carotid noid (termed the planum sphenoidale). This depression corresponds to pneumatization of the optic course of the carotid in the lateral wall and the areas where strut (the bony bridge that separates the optic canal from the supe- extra care needs to be taken. Further pneumatization into the optic strut may result in a pneumatized anterior clinoid process which will place the optic nerve on a mesentery. If the surgeon enters the cavernous sinus from the pituitary fossa this is usually following a tumor extension through the dura above the horizontal portion of the cavernous carotid and posterior to the anterior genu (Fig. As the cavernous ca- rotid forms the anterior genu and becomes the clinoid carotid, the tumor may envelop this as well. It is usually not possible to chase tumor above and lateral to the clinoid carotid. If tumor grows anterior and lateral to the anterior genu of the cavern- ous carotid, the cavernous sinus may be entered via a separate incision through the dura lateral to the anterior genu. Great care should be taken with this incision and the surgeon should confrm the position of the carotid with image guidance as well as an intranasal Doppler. Gentle suction clearance of tumor in this region will often reveal the third nerve lateral and superi- Fig. Inferiorly in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, the Gasserian ganglion and its branches V1, V2, and V3 can be seen (Fig. Note the cavernous sinus is always above V2 which does leave an anatomical pathway under V2 into the middle cranial fossa (Fig. It can often be seen in a well pneumatized sphenoid as it forms an inferior ridge in the foor of the sphenoid (Fig. It forms an important lateral boundary when surgeons remove the foor of the sphenoid in preparation for approaching the clivus Fig. If the vidian nerve is followed posteriorly it initially removal of the lateral sphenoid wall. Dissection has continued anteriorly approaches the supralacerum genu of the carotid artery at its to the pterygopalatine fossa inferiorly and the orbital apex superiorly. In medial aspect but then moves laterally and over the top of the this image the periorbita has been retracted superiorly. In this dissection a “leaf” of periosteal dura has been of the supralacerum genu of the carotid artery, where the horizontal incised and refexed to clearly visualize the abducens nerve running petrous carotid artery turns upward to become the paraclival carotid within. The vidian canal and nerve is a vital landmark in surgical of the superior and inferior petrosal sinuses, the basilar plexus, and the dissection in this area. The thickness of the bone of the clivus varies depending on the pneumatization of the sphenoid. The frst step in transclival approaches to the posterior fossa is to accurately identify both paraclival carotids. These can bleed ex- tensively and often require the dura to be opened, rolled, and bipolared to stem the bleeding. Additionally, Gelfoam paste or Surgifo is used with neuropatties in an attempt to fll these venous lakes and stem the bleeding. One of the most important structures encountered in this region is the sixth nerve. The sixth nerve leaves the pons just lateral to the vertebrobasilar junction, and moves laterally, tra- versing the post fossa (termed the cisternal segment) until it enters the dura (at Dorello’s point) and runs between the Fig. From here it enters the superior orbital fssure and into A good landmark is the dorsal meningeal artery found the orbit. Another landmark includes the distance from the poste- rior clinoid, which averages 20 mm and usually 10 mm from the midline. This venous plexus is formed between dura and periosteum and is made up from the inferior petro- The mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve leaves the sal venous sinus, the posterior part of the cavernous sinus, cavernous sinus from the Gasserian ganglion and proceeds and the basilar venous plexus. These all join in this region horizontally toward the foramen rotundum and the ptery- and the nerve runs in the foor of this so-called gulfar seg- gopalatine fossa. Another landmark in this area is the sphenopetrosal well-defned ridge in the lateral wall called the trigeminal ligament (Gruber’s) that is formed from the posterior cli- impression (Fig. The sphenoid may also pneumatize noid process and lateral aspect of the dorsum sella to the under the nerve thinning the bone between the sphenoid petrous apex. This pneumatization may also ernous sinus below the horizontal portion of the cavern- develop into the upper root of the pterygoid plates. This thin ous carotid, it travels forward and hugs the inferior aspect plate between the middle cranial fossa and a laterally pneu- of the anterior genu of the carotid before traversing the matized sphenoid is a common site for prolapse of dura and cavernous sinus on the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. Endoscopic Resection of Clival and 19 Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors Tumors of the clivus and posterior cranial fossa are very dif- Anatomy fcult to access via traditional neurosurgical approaches. In the past skull base teams would approach the petroclival The Clivus region either by a lateral or anterior route. The lateral route was via an extended middle cranial fossa approach1 whereas The clivus extends from the dorsum sella to the foramen mag- the anterior route could be transmaxillary, transoral, or num (Figs. The operating microscope process as signifcant bleeding can occur as the cancellous did not allow a view around the corner and, if the tumor bone is opened. This is generally quickly controlled by packing extended beyond the exposed area, resection under direct the area with Gelfoam paste (Pharmacia and Upjohn Company, vision was not possible.
Thus buy generic oxcarbazepine 150 mg on line medicine 802, desmin is uniquely situated to integrate signals from both cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions to ensure cellular integrity purchase oxcarbazepine with amex medications post mi, force transmission buy oxcarbazepine 600 mg with visa ad medicine, and biochemical signaling (35). Given this crucial role, it is not surprising that mutations in desmin lead to cardiomyopathy (87). The gap junctions maintain electrical coupling of individual myocytes to form an electrical syncytium. Gap junctions ensure the proper propagation of the electrical impulse, which triggers sequential and coordinated contraction of the myocardium. These isoforms also exhibit distinct regional, cell type–specific and chamber-specific expression, with different isoforms present in the conduction system as compared to the ventricular myocardium (90). Six connexins combine to form one connexon that extends from the plasma membrane of one cell to dock with a connexin of an adjacent cell, creating an intercellular gap (88). B: Expression of Cx43 (green) and α-actinin (red) at different stages of human cardiac development. Cx43 progressively relocalizes from the myocyte lateral membrane toward the intercalated disc (Upper left, 10. Arrows indicates less intense staining in the intercalated disc at the age of 5 years compared to the intensity of lateral signals. Assembly of the cardiac intercalated disc during pre- and postnatal development of the human heart. Gap junction channel assembly, membrane localization, gating, and degradation are regulated by a variety of stimuli including voltage, ionic concentrations, pH, phosphorylation, and local protein interactions. During cardiac myocyte development and maturation, large changes in the spatiotemporal distribution of gap junctions, desmosomes, and adherens junctions occur. In the mature myocardium, all three are clustered in a bipolar pattern (perpendicular to the long axis) on the ends of the myocyte. However, during embryologic development, adherens junctions are also found on the lateral membranes where they seem to be able to sense mechanical forces along the transverse axis and are thought to play an important role in myofibrillogenesis (63,93). At the perinatal stage, the adherens junctions no longer surround the entire cell, but are restricted to intercalated discs between cells. Interestingly, this polarization coincides temporally with an increase in cardiac output at birth to support the needs of the newborn, suggesting that maturation of contractility provides mechanical inputs for cadherin movement to the longitudinal border (63). Most of the adherens junction proteins were completely localized to the intercalated disc by 12 months after birth (Fig. In contrast, there was sparse, diffuse connexin-43 expression in fetal hearts that gradually increased after birth but does not fully segregate to the intercalated disc until 7 years of age (94). The functional implications of these differences are unclear, but may partially explain the ability of neonatal cardiac myocytes to propagate electrical impulses in both the longitudinal and perpendicular axes (“isotropic”), compared to the “anisotropic” adult myocytes that predominantly exhibit longitudinal impulse conduction (94,95). Several cardiac disorders have recently been identified in which defective electromechanical coupling between cardiac myocytes leads to degenerative cardiomyopathies characterized by contractile impairment and electrical disorders. Mutations in proteins in the adherens junctions are associated with heart failure and dilated cardiomyopathy (84). Coronary Vasculature The spontaneously contracting heart tube is initially formed as an avascular organ. The cells that form the tissues of the coronary system move onto the surface of heart after the looping stage of cardiogenesis, making first contact at the future site of the atrioventricular septum. The specific origins of the coronary endothelial cells have been the rigorously debated; as a number of different approaches for determining their origins have resulted in conflicting conclusions (99,100,101). Regardless of the cellular origins, the signals that regulate coronary development are derived from both the epicardium and cardiac myocytes (99). Both metabolic (hypoxia) and mechanical factors stimulate growth factors that promote angiogenesis (102). The coronary vessels begin to coalesce from mesenchymal cells via vasculogenic processes in the extracellular matrix-rich, subepicardial space between the epicardium and the myocardium (105). The subepicardial space is not only the initial site of coronary vessel formation, but also the site of large-caliber coronary vessels in adults. Coronary vessels form as blood cell–filled cul-de-sacs until capillary projections from these vessels surround and become patent with the aorta (106,107). Once aortic perfusion has been established, these capillary beds quickly remodel into the left and right main coronary arteries and subsequent coronary vessels. In rodents this remodeling of capillary beds into muscular arteries happens over the course of hours. The signaling mechanisms that direct early coronary capillary beds to surround the aorta instead of the other great vessels such as the pulmonary artery are not clear. Nor is it unclear how the cusps are selected for coronary artery investiture and why one cusp is avoided. The noncoronary cusp is deeply embedded in the atrioventricular septum, specifically the annulus fibrosus, and thus the capillary beds have limited access to this sinus of the aortic valve. However, how atypical coronary vascular patterns affect cardiac performance or health are not always clear. It is generally thought that once formed, the coronary vessels sprout from their location in the subepicardial space and dive into the forming compact myocardium so that each cardiac myocyte is proximal to a capillary via angiogenic processes. Presumably, hemodynamics drive the rapid remodeling of the coronary capillary beds into the large-caliber main coronary arteries and the formation of the coronary system. Physiologic feedback between the myocardium and coronary vessel development is also affected by mechanical stimuli. As blood flows through the developing vessels, endothelial cells are exposed to shear stress, which is a function of fluid flow velocity and viscosity. Endothelial cells are equipped with a variety of “mechanosensors” that respond to shear stress and stimulate the expression of a variety of genes required for endothelial function and differentiation of arteries and veins (111). In humans, the number of arterioles and capillaries steadily increases during the first postnatal year (112). Myocardial Growth and Remodeling Cardiac myocytes display two types of growth during the fetal and neonatal transitioning from a proliferative phase to a hypertrophic phase. After their formation, the myocardial cells of the primitive heart tube undergo region-specific growth that drives cardiac morphogenesis (115). During this proliferative phase, mitosis and cell division are coupled as the myocardium rapidly expands. A second wave of mitosis without cytokinesis follows this phase and generates binucleated cardiac myocytes (116,117). Thus, myocardial growth transitions from cell division to cell hypertrophy during the perinatal period. An intermediate phase is associated with the binucleation of cardiac myocytes, which are particularly evident in ventricular myocytes (116). As cardiac myocytes are exiting the proliferative growth phase during the postnatal period, the myocardial mass dramatically increases. At the cellular level, cardiac myocytes are growing via hypertrophic mechanisms, adding sarcomeres in series (lengthwise) and in parallel (widthwise) (121). Also during this phase of heart development, interstitial fibroblasts begin to increase in cell number, becoming the predominant cell type of the myocardium (122).