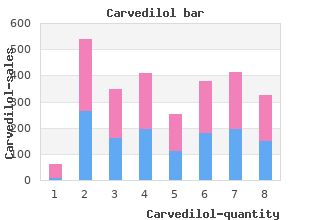


Palmer College of Chiropractic. N. Trano, MD: "Buy Carvedilol online - Trusted Carvedilol online no RX".
Glaucoma Ciene Research potassium adm inistration on intraocular pressure in norm otensive Group buy 12.5mg carvedilol with amex pulse pressure definition. Association between glau growth factor-П in transgenic m ice is associated with pancreatic coma and gene polym orphism o f cndothclin type A rcccptor buy generic carvedilol canada heart attack what everyone else calls fun. Regulation of cndothelin-1 arrest in colon canccr ccll exposed to phenolic antioxidant cllagic hum an nonpigm cntcd ciliary epithelial cells by tum or necrosis acid 25 mg carvedilol visa hypertension uncontrolled icd 9 code. M 1 positive genotype afford protection against prim ary open-angle Mol Vis 2003,9:103-109. Oxidative deoxyribonucleic acid adrenoccptors in im m ortalized hum an trabccular m eshwork and damage in the eyes of glaucoma patients. Polymorphism of bcta-adrcn- m ary open-angle glaucoma: a study in a Turkish population. Beta l-adrcncr- S-transferase M l is a risk factor of prim ary opcn-angle glaucoma gic receptor polym orphism s confer differential function and pre am ong Estonians. Arg389Gly polym orphism of lon4 gene is associated w ith elevated risk of norm al tension glau the hum an beta 1-adrenergic receptor m patients with nonfatal coma. Apoptosis o f retinal ganglion cells in glaucoma: an protcin E genotypes with prim ary open angle glaucoma and pri update o f the m olecular pathways involved in cell death. High level expression o f delt- E gene polym orphism s in prim ary open-angle glaucoma. Arch aX-p63: a m echanism for the inactivation of p53 in undifferentiated O phthalm ol 2004;122:258-61. The C677T variant in the canccr by an adenovirus expressing a novel tum or suppressor gene, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene is not associated with dis pHydc. Tum or necrosis factor-alpha: a potentially prom oter m utation in prim ary open angle glaucom a patients. Hum neurodestructive cytokine produced by glia in the hum an glau G enet 2000;107:404-5. Matrix m ctalloproteinasc and tum or gene in the etiology of prim ary open angle and exfoliative glau necrosis factor a in glaucomatous optic nerve head. Cloning, modeling, and chrom o signals induction of nitric oxide synthase-2 in hum an optic nerve somal localization for a small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycan (Sl. Induction of heat shock protein m ouse retinal ganglion cell layer is induced in vivo by the excitatory 72 protects retinal ganglion cells in a rat glaucoma model. Immunolocalization of heat mcthylcntetrahydrofolate reductase gene is a genetic risk factor for shock proteins in the retina of normal monkey eyes and monkey eyes prim ary opcn-anglc glaucoma. Association of an interleukin 1 alpha pseudoexfoliation syndrom e and pscudoexfoliation glaucoma. This is followed by an invagination into the although the association with other ocular and systemic optic cup referred to as the lens pit at 29 days of gestation. The epithelium proliferates to differentiate and recessive inheritance patterns have been documented. Л classification of the most frequent subtypes of congenital New fibers arc added to the fiber mass throughout life (creat cataracts is provided in Table 19. Any deregulation in these mechanisms leads to formed retina and non-development of lens,” while an loss of transparency of the lens, resulting in variable degrees absence of lens results in loss of vitreous volume leading to of opacification. The past two decades Using animal models, various developmental genes have provided an extensive amount of information on the were found to be expressed in the lens at different stages of genetics of inherited cataracts, which present a significant growth and development. Congenital cataracts due to other causes, such as infection (rubella, syphilis, toxo When the newly formed lens fibers elongate posteriorly, the plasmosis), trauma, and drugs, will not be discussed. The a crystal lins are synthesized in the epithelial cells, while the struc Associated to See Table 19. The gcnetic background of Weiii-Marchesam syndrome inherited cataracts is highly heterogeneous and their Craniofacial HallermanivStreifr syndrome underlying genetic characteristics remain incompletely malformations Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome characterized to date. Various genes play a role in lens development, and a ВЮск-SuizberRer syndrome mutation in one or more of these genes can result in lens Ichthyosis opacity associated or not with various other ocular malformations such as anterior segment dysgenesis, iris Chromosomal Numeric Trisomy 8. Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant und interaction between ectoderm and keratitis. Mutations that severely disrupt protein function a critical role in the maintenance of lens transparency. W hen mutations More of these genes and protein functions are yet to be affect protein function only mildly, a less severe form of the fully characterized. Mutations in modification in their structure, causing loss of transpar the same gene as well as the same mutation in one gene ency and leading to scattering of light. These the person and the environment constituted 38% and 14% recurring observations limit the usefulness of molccular respectively. The study important, with heritability contributing 53% to 58% of of additional large pedigrees with affected and unaffected cataract risk and environmental factors explaining 26% to individuals will provide an opportunity to further charac 37% of variance. Unlike nuclear cataracts, the age of a terize phenotype variability and possibly identify novel person explained only 1 1 % to 16% of the variance of corti cataract genes and mutations. Although there has been an improvement in the understanding of the nature of adult- Several epidemiologic studies have shown clear evidence onset cataract using genetic and molecular biology tech that genetic factors contribute to the pathogenesis of nologies, more work is warranted to dissect the complex Е ngure 19. Retroillumination view of a typical epinuciear opacity related to hyperferritinemia in Diseases In a stable patient with known poison exposure buy carvedilol overnight delivery blood pressure medication and weight gain, who is breathing spontaneously with intact protective airway generic carvedilol 6.25mg mastercard hypertension goals jnc 8, should be managed without intubation discount carvedilol 6.25mg fast delivery arteria3d mayan city pack. Anticipatory intubation is indicated in poisoned patients because they are at high risk for progressive and sudden respiratory failure. In patients where prolonged admission is anticipated, central vein may be secured. Removal of contaminated clothing, flushing the skin and mucus membranes with water are the first priorities once the cardiorespiratory status is stabilized. Reassess the child for appearance of stridor, edema, or respiratory distress and treat accordingly. Combination of any of the methods will be used depending on type and amount of toxin consumed, time elapsed since consumption. It can be used only in a child more than six months old, who is alert, and unlikely to deteriorate and has taken tablets that are enteric coated or extended release, and are unlikely to be removed by gastric lavage. It is strongly contraindicated in child less than six months, comatose or obtunded, or has consumed corrosives or hydrocarbons, has already vomited, or has a history of co-consumption of a sharp foreign body. Complications of ipecac-induced emesis include esophageal tears, fever, lethargy, diaphoresis, and aspiration. It is not useful in removing intact pills or large fragments especially in small children. First gastric aspirate may be useful to identify toxins and can be submitted for laboratory analysis. The potential complication include wrong placement of catheter in trachea, esophageal injury, hypothermia, hyponatremia, water intoxication. It is an inert, nontoxic and non-absorbable material with vast surface area comprising fine network of pores. The adsorptive capacity of activated charcoal ranges from 1000 to 2500 m2 per gram. If administered within an hour, activated charcoal can reduce the absorption of the toxins up to 75 %. It is given as slurry in a dose of 1 gm/kg diluted with fruit juice or bottled drinks orally or through orogastric tube in an unco-operative child. However, while using multiple doses repeated doses of cathartics should not be used to avoid risk of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. It is useful in many toxins like theophylline, phenobarbitones, and carbamazepines. Out of stimulants, osmotic agents and bulk forming agents, only osmotic agents are used in poisoning. In general they are not used in younger children or with underlying renal disorder as they might cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and in case of magnesium based cathartics, hypermagnesemia. Commonly used cathartics include sorbitol (1 gm/kg), magnesium sulfate (250 mg/kg) and magnesium citrate (250 mg/kg). It should be used cautiously in small children for risk of fluid and electrolyte imbalance. However, drugs that are highly protein bound or having high volume of distribution cannot be dialyzed. Although hemodialysis is generally more efficient at removing toxins, peritoneal dialysis is often easier to perform in young children and may be sufficient. Few drugs or toxins are removed by dialysis in amounts sufficient to justify the risks and difficulty of dialysis. Examples of toxins for which dialysis may be useful include methanol, ethylene glycol, and large symptomatic ingestions of salicylates or theophylline. Theoretically, it is a dialytic technique in which blood is passed through a column of activated charcoal or resin. Hydrocarbons are easily accessible in products such as gasoline, turpentine, furniture polish, household cleansers, propellants, kerosene, and other fuels. Most of the dangerous hydrocarbons are derived from petroleum distillates and include aliphatic (straight-chain) hydrocarbons and aromatic (benzene-containing) hydrocarbons. Direct contact with alveolar membranes can lead to hemorrhage, hyperemia, edema, surfactant inactivation, leukocyte infiltration, and vascular thrombosis. Respiratory symptoms generally begin in the first few hours after exposure and usually resolve in 2-8 days. Etiologies include hypoxia, myocardial sensitization to catecholamines, and direct myocardial damage. Sudden death has been reported as a result of coronary vasospasm due to hydrocarbon inhalation. Physical: In cases of hydrocarbon aspiration, the patient’s temperature may be elevated due to the body’s reaction to the foreign substance. Imaging Studies: • Chest radiography – A chest radiograph must be obtained in all symptomatic patients. Medical Care: • Airway, breathing, and circulation: Stabilization of the airway is always the first priority of treatment. Early intubation, mechanical ventilation, and use of positive end-expiratory pressure may be warranted in a patient in whom oxygenation is inadequate or in a patient who has severe respiratory distress or a decreased level of consciousness. Take all precautions to minimize the patient’s risk of vomiting and further aspiration. Any change in the patient’s clinical respiratory symptoms warrants repeat chest radiography, which may demonstrate new and important changes. Clean the skin as soon as possible by removing the involved clothing and thoroughly washing the skin with soap and water. Health care providers must take precautionary action to minimize their own exposure to the toxic substance. Lavage is useful in cases in which the hydrocarbon has an inherent systemic toxicity or contains additives with known toxicity. Activated charcoal is indicated only in cases of a suicide attempt or in cases in which another adsorbable toxic substance have been co-ingested. Exposure Organophosphates are very efficiently absorbed from the skin and mucous membranes. The majority of organophosphate poisoning occurs by accidental or occupational exposure, but poisoning may also be due to suicide attempts, homicide attempts, or chemical warfare. In a child less than one year of age with an organophosphate poisoning, child abuse or neglect may be suspected. In anyone older than 6 years of age, a suicide attempt should be considered in the differential. Healthcare workers must be very cautious to prevent self-contamination when caring for an exposed patient. When caring for a patient with organophosphate poisoning, it is important to remember than any vomited material should be treated as a chemical spill. Pyelonephritis Description: Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney and renal pelvis purchase carvedilol 6.25mg line blood pressure medication for asthmatics. T1-weighted fat-suppression images may show proteinaceous material in the renal tubules as high-signal substance purchase discount carvedilol line pulse pressure norms. Treatment: All symptoms usually resolve within 72 hours following administration of the appropriate antibiotic therapy effective 6.25 mg carvedilol phase 4 arrhythmia. Renal Artery Stenosis Description: the most common cause of correctable hypertension is stenosis of the renal artery. Hypertension of the renal artery can occur as a result of either atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. Etiology: Results from the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques or fibromuscular dysplasia in the renal artery. Fibromuscular dysplasia causes a beading (string of pearls) appearance and involves the distal two-thirds of the renal artery as well as other peripheral branches. Treatment: Methods of treatment include angioplasty, stenting, and surgical revascularization. Renal Calculus Description: Renal calculi (kidney stones) may form anywhere throughout the urinary tract. Etiology: the exact cause is unknown; however, predisposing factors include dehydration (increased concentration of calculus-forming substances), infection (changes in pH), obstruction (urinary stasis, such as may be seen in spinal cord injuries), metabolic disorders (e. Epidemiology: Renal calculi result in roughly 1 per 1000 hospitalizations annually. Signs and Symptoms: Patients may present with back pain (renal colic), pain radiating into groin area, hematuria, dysuria, polyuria, chills, and fever associated with infection due to obstruction, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distention, and costovertebral angle tenderness. Treatment: Treatment includes pain management, fluid management, straining urine for urine analysis and stone collection, and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Prognosis: A good prognosis is expected with complete return to the patient’s previous state of health. Etiology: the cause of renal cell carcinoma is unknown; however, it is known to arise from the proximal convoluted tubule. Epidemiology: Approximately 30,000 new cases are diagnosed annually with about 12,000 deaths. The average age of occurrence appears between the fifth and sixth decades of life. Signs and Symptoms: Patients may present with a solid renal mass (6 to 7 cm), hematuria, abdominal mass, anemia, flank pain, hypertension, and weight loss. Postcontrast T1-weighted images appear hyperintense with heterogeneous enhancement. Treatment: Surgical removal of the kidney (nephrectomy) when the cancer is confined to only one kidney. Postcontrast axial T1W image shows enhancement of the solid portions of the left renal mass. T2W image shows areas of increased signal in the mass consistent with central necrosis of the renal cell carcinoma. Renal Infarct Description: A renal infarct is a localized area of necrosis in the kidney. Etiology: An acute infarct of the kidney may follow a thromboembolic (most common), renal artery occlusion (due to atherosclerosis), blunt abdominal trauma, or a sudden, complete renal venous occlusion. Epidemiology: the most common cause of renal emboli occurs in patients with atrial arrhythmias or patients who have a history of a myocardial 362 infarction. In addition, patients who have experienced blunt abdominal trauma may develop renal emboli. Signs and Symptoms: This condition may go unnoticed; however, some patients may experience pain with tenderness in the region of the costovertebral angle of the affected side. Convention renal arteriogram is the gold standard for the evaluation of an occlusion of renal artery or its branches. T1-weighted postcontrast images demonstrate a wedge-shaped low- signal area of the renal parenchyma. Wilm Tumor Description: the most common type of renal cancer in children and the fifth most common cancer affecting children is a Wilm tumor. Wilm tumor may also be called nephroblastoma (a malignant tumor arising from the 364 embryonic kidney). About 80% of this tumor presents between 1 and 5 years of age, with the peak age at the time of diagnosis between 3 and 4 years old. Hypertension, hematuria, and anemia are other signs and symptoms associated with Wilm tumor. Imaging Characteristics: Ultrasound initial modality of choice, especially for pediatric patients and radiation dose. Helpful in staging and metastatic spread (lung metastases are more frequently involved than the liver). Prognosis: With appropriate therapy and early detection, a good outcome is expected. Epidemiology: Appendicitis can occur at any age and affects males and females equally. Signs and Symptoms: Patient may present with abdominal pain or tenderness in the right lower quadrant (McBurney point), anorexia, nausea and vomiting, and constipation. If the appendix ruptures, there is a variable degree of morbidity and mortality based on the age of the patient. Diverticulitis is an abscess or inflammation initiated by the rupture of the diverticula into the pericolic fat. About 40% to 50% of the general population is affected by the time they reach their sixth to eighth decades of life. When considering diverticulitis, in addition to the above, patients will experience fever with chills, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, and tenderness in the left lower quadrant. Prognosis: With early detection and treatment the patient should experience a good recovery. Perinephric Abscess 370 Description: A perinephric abscess is a collection of pus within the fatty tissue around the kidney. Epidemiology: Perinephric abscesses usually arise from a preexisting renal inflammatory disease. However, they may occur as a result of complication of surgery and trauma, or spread from other organs. Signs and Symptoms: Patients will present with flank or back pain, fever, nausea and vomiting, malaise, and painful urination. Treatment: Intravenous administration of antibiotics and percutaneous catheter drainage. Epidemiology: Most renal abscesses are the result of an ascending infection and are usually due to gram-negative urinary pathogens, in particular E. Nystagmus order carvedilol 12.5mg overnight delivery heart attack arena, agitation purchase carvedilol canada arteria profunda femoris, amnesia buy carvedilol without prescription understanding prehypertension, abnormal vision, ataxia, confusion, Fify-three per cent of 229 patients on 2 g/day vigabatrin and 57% psychosis, depression and diarrhoea have also been reported [100]. However, signifcantly more patients on vigabatrin with- dation, insomnia, hyperactivity, agitation, weight gain and hyper- drew due to lack of efcacy than with carbamazepine, and time to tonia or hypotonia [35,42,91,92]. Most of these adverse efects are frst seizure afer the frst 6 weeks from randomization also showed dose-related and reversible when the dose is reduced. Formal testing of mood disturbances in 73 adults with refrac- genic and symptomatic cases. In two of the studies, allocation to tory epilepsy treated with vigabatrin revealed that mood problems treatment was randomized [85,86]. In all three trials, the efcacy of were the main reason for discontinuation of the drug [104]. A re- vigabatrin and carbamazepine did not reveal signifcant diferences, view of double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of adjunctive vigab- and there was a suggestion for a better tolerability profle of vigaba- atrin therapy in a total of 717 patients with refractory focal epilepsy trin during the 2-year follow-up [86]. Tese studies have limitations confrmed that vigabatrin, when compared with placebo, was as- because of their small sample size and lack of blinding, but they sociated with a signifcantly higher incidence of depression (12. Depression was usually mild, and psychosis was re- Generalized epilepsies ported to respond to reduction or discontinuation of vigabatrin or An early multicentre study assessed outcomes of add-on therapy to treatment with antipsychotic drugs. Efcacy was better in children with focal seizures than in those pected, amino acid chromatography should be performed before with generalized seizure types. In addition, vigabatrin can gabatrin more efcacious against focal seizures [89,90], although interfere with urinary amino acid analysis due to inhibition of ca- this has not been an invariable fnding [91]. Visual feld constriction Anecdotal case reports described favourable efects of vigaba- Severe symptomatic visual feld defects associated with vigabatrin trin in neonatal seizures due to Ohtahara syndrome [93]. A further 674 Chapter 52 120 105 90 0 70 135 45 60 50 30 150 40 30 165 15 20 10 180 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 0 30 10 20 195 345 30 40 210 50 330 60 225 70 315 240 255 270 285 300 Figure 52. Usually, the constric- Reported prevalence data for vigabatrin-associated visual feld tion of the visual feld is concentric, afects both eyes and is gen- constriction in children are variable, presumably due to diferences erally more marked nasally than temporally (Figure 52. In the in perimetric techniques and difculties in ensuring the child’s co- central visual feld (within 30 degree of eccentricity), frequently an operation. Several studies using Goldmann perimetry or the Hum- annular nasal defect can be observed [110]. The visual defects are phrey feld analyser in patients aged 5–21 years found prevalence irreversible. The prevalence of vigabatrin-induced visual feld constriction [52] performed Goldmann perimetry tests in 91 visually asympto- varies depending on age, gender, extent of exposure to vigabatrin matic Finnish children aged 5. Because of slow development of the visual constriction in repeated test sessions in 17 children (18. A total of 734 patients exposed to vigabatrin (44%) had cluding 49 aged 8–12 years) treated with vigabatrin for >6 months, visual feld loss compared with 30 (7%) vigabatrin-naïve patients. Perimetric testing was performed every 6 months for up to for patients with greater mean cumulative dosage and older age. In group I, visual feld constriction at the last visit with a small study which reported serial monitoring of 14 adults exposed a conclusive examination was diagnosed in 31. Visual feld degree of variability in visual feld size between successive test ses- constriction was signifcantly associated with duration of vigabatrin sions. Tere was a trend for visual feld constriction to be less in three and severe in four cases). Overall, these data indicate that frequent in the younger age groups, but the statistical power of the the risk of peripheral visual feld constriction afer vigabatrin ex- comparisons was limited by the small size of the subgroups. In con- posure during early life is low when duration of treatment is short clusion, approximately one-third of patients aged ≥8 years exposed and cumulative dose is low. However, the risk increases rapidly with to vigabatrin exhibited visual feld defects which were not encoun- treatment duration over 2 years. The study did not include infants Tere has been considerable interest in monitoring electroretino- with infantile spasms. All school-age patients were tested es induced by vigabatrin include increased latency of the photopic with Goldmann kinetic or Humphrey static perimetry and a stand- b-wave, reduced or absent oscillatory potential, abnormalities of ard ophthalmologic examination. Among 67 children aged 3 months to 13 years ex- visual feld constriction [118,119]. Among children treated for patients, and abnormal scotopic log σ and photopic b-wave implicit 12–24 months (mean cumulative dose 758. In the latter study, a subset 676 Chapter 52 of 39 patients also underwent perimetry which did not show sig- [135,136,137,138]. Post mortem that minimizing vigabatrin treatment to 6 months will reduce the neuropathologic examination in the second case revealed white prevalence of retinal dysfunction in patients with infantile spasms. Although intramy- The pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying the retinal toxic- elinic oedema has been reported in preclinical toxicology studies, ity of vigabatrin are still under investigation. A study using optical the neuropathologic fndings in that infant seem to be exceptional. Histopathological fciency may facilitate retinal ganglion cell loss as well as photore- fndings in 10 post mortem and 50 surgical samples of patients ceptor damage and disorganization of the photoreceptor layer and with an estimated 350 000 patient-years of vigabatrin exposure also gliosis during exposure to vigabatrin [127,128,129]. Interestingly, failed to identify any defnite case of vigabatrin-induced intramy- a small retrospective human study found reduced plasma taurine elinic oedema or vacuolation [142]. Symptoms static perimetry seems to be the most sensitive modality for iden- occurred with a latency of 2–5 weeks [140,143] and 6 months [144] tifying vigabatrin-induced visual feld constriction [115]. In the three infants who became symp- feld constriction is not ascertainable in infants, young children tomatic within 5 weeks, symptoms resolved afer vigabatrin with- and patients with severe mental disability. Among 124 patients included in the International Collab- method based on feld-specifc visual evoked potentials is available orative Infantile Spasms Study, 10 (eight on vigabatrin treatment) from the manufacturer on request to test for the presence of pe- developed a movement disorder, and in only two of those was a ripheral vision in children aged 3 years and above [110]. The copy shows no specifc abnormalities until the visual feld loss is authors of the latter report felt that there was no direct link between severe. Although there are cording to the European prescribing information are discussed in insufcient data to determine risks for human fetal development, the ‘Place in current therapy’ section. A useful algorithm for the vigabatrin is not recommended in women of childbearing potential ophthalmological assessment of patients treated with vigabatrin has [145]. One child had dysmorphic features, This includes a registry collecting data about the occurrence, pro- and the other had several major congenital malformations but had gression and severity of vision loss for patients treated with the drug. Rapid control of spasms could reduce the risk of epileptic Vigabatrin 677 encephalopathy and minimize the deleterious efect of seizures and 13. Epilepsy Res ment of focal seizures, with or without secondary generalization, 1988; 2: 96–101. Vigabatrin: placental transferin vivoand excre- risk of visual feld defects, its role in the treatment of focal seizures tion into breast milk of the enantiomers. Vigabatrin for refractory complex par- tial seizures: multicenter single-blind study with long-term follow-up. Pharmacokinetics of may be reduced by limiting the duration of vigabatrin treatment vigabatrin: implications of creatinine clearance. Pharmacokinetics of the individual enantiomers of vigabatrin in neonates with uncontrolled seizures. Buy 25mg carvedilol amex. NATURAL CURES FOR HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE THAT YOU CAN USE TODAY.