

Olivet Nazarene University. N. Mufassa, MD: "Order cheap Gabapentin online no RX - Discount Gabapentin no RX".
This has implications in particular for relationships at work and how people are viewed (and treated) by colleagues buy gabapentin 100 mg low cost treatment 4 anti-aging. Thats often a criticism of depressed people gabapentin 400 mg without prescription medications 3605, people say oh its like youre in a really bad mood all the time purchase 400mg gabapentin with amex treatment 3rd degree burns, cheer up, whats the matter with you? Such difficulties with relationships and interactions at work might be exacerbated by lack of sleep and general tiredness. Further, this was seen as problematic in terms of an individuals ability to attend work on time. Some of them actually struggle to get to work in the morning which means that they have their employer ring them to say that they havent turned up to work. It might be because theyve had a terrible nights sleep or just for the fact that they cant face coming to work. Distorted or negative thinking can cause people to interpret things more negatively than they otherwise might, for example, feeling that they are not very good at their job, believing that their employer and colleagues think this or feeling overly criticised. Its always the worst possible explanation for a series of events and always thinking the Symptoms of depression and their effects on employment 9 worst, not giving people the benefit of the doubt, always assuming the worst. It was suggested that often people experiencing these symptoms lose confidence in their ability to do their work, causing them to worry about failure and avoid certain tasks (or avoid work altogether). This worry might be so distracting as to affect work performance or self esteem might be affected to the extent that work is affected. This perception of failure can therefore become a self-fulfilling negative cycle. You would probably think they were doing their job quite well but they feel like theyre not and even if you say no, no, youre doing it fine, its quite hard for them to accept and believe that. Low self-worth and self- efficacy are often experienced by people with depression. It was suggested that often people find themselves unable to imagine that someone would want to employ them lowering their motivation to seek work even further and perhaps feeling a sense of hopelessness. Theres the sort of worthlessness and hopelessness part of depression and the drain on your own sort of self-esteem and morale. Your energy is reduced, youre tired, I dont feel like it, how am I going to work if I cant even get out of bed in a morning? One expert suggested that to find a job requires a positive mind-set as job seekers need to put themselves out there. This will be a considerable challenge for someone experiencing this type of negative cognition. Here the very nature of the condition can be seen as a barrier for engaging in job seeking. So the whole selection and recruitment process is geared on people who have got a positive world view, a positive outlook who can project themselves well. If low self-esteem is part of your depression, given the current way in which people are recruited to jobs, youre probably all things being equal not going to do that well. Symptoms such as poor concentration, indecision, and difficultly planning and prioritising (many of which are seen as cognitive symptoms) were raised by experts; described most often in terms of job retention. Poor concentration was mentioned most often associated with making mistakes with work, difficulty with following processes or instructions or getting distracted and losing your place during your task. When youre there at work if your concentration and attention span is reduced, youre often not able to do things for long periods or even start the job in the first place. Where there is a lot of change in an organisation or a requirement to learn new processes this was seen as particularly problematic with reversion to old ways and previously retained information a possibility. One expert also highlighted slowed processing, emphasising that there may be difficulties where tasks are time restricted. Peoples reaction times are often slower; there are often delays in processing as well. So work tasks which may be time restricted, people find it very difficult and struggle in terms of completion of those tasks they cant meet targets in the way that they might have ordinarily. One expert identified that often cognitive-type symptoms of depression are late to respond to conventional treatment, continuing as residual even though other symptoms may be in remission. They are to a large part invisible and may therefore go recognised and untreated. This has particular implications in the workplace, for example, where employers are not aware that an individual is still experiencing symptoms of depression and instead see reductions in work performance as a performance management issue rather than as a result of continuing untreated symptoms. I think often people end up in the performance management arena, rather than supportive what can we do to help your symptoms arena. Experiencing cognitive-type symptoms and being aware of how they are affecting work performance may have secondary consequences for the individual. It was suggested that the frustration for an individual in recognising a change in their abilities can be a source of further stress and anxiety. Where people previously functioned at a high level and theres a secondary irritation, an anxiety that these symptoms have emerged and it makes them feel as if they might not get better. This awareness of not being able to work as productively as previously may cause an individual to worry that they are less proficient at their job, or at any job, and exacerbate negative beliefs about self and work feeding into the negative cycle. So theyre aware that their cognitive symptoms are causing them to struggle and therefore that makes them Symptoms of depression and their effects on employment 11 avoidant about going back to work. These types of negative belief, which might be exacerbated by cognitive symptoms, may lead someone to believe that they are unemployable with considerable implications for job retention, as well as for job seeking. What happens of course is that people, because they have a very low self-worth and self- esteem, and often their sense of self efficacy is so low, they find it hard to imagine anyone would want to employ them. One expert suggested that for those who are unemployed, symptoms might be exacerbated by the lifestyle of unemployment associated with low activity, poor self-care and reduced motivation to get up in the morning. If the individual perceives their unemployment as personal failure then this may further reduce feelings of self-worth, feeding into their depression. Another perspective offered by one expert was about how physical symptoms of depression affect employment. This might be seen in two ways either in terms of the physical manifestations of poor mental health, for example a bad back, or in terms of someone explaining their sickness absence by telling employers (and clinicians) that they have a physical condition to avoid admitting they have depression, given the considerable stigma around mental health. On the other hand the physical symptoms of depression quite often are what masks the underlying mental health state. People often say theyre off because of back pain when the real reason theyre off is something thats less palatable to put on a sick certificate; its actually depression, not their back pain. Summary and conclusions In light of evidence from the questionnaire studies included in the literature review (involving 6 46,513 individuals of working age with depression ), it is possible to conclude that there is strong and mainly consistent evidence that cognitive dysfunction and other symptoms of depression have negative impact on employment outcomes of people with depression. There is moderate and mixed evidence that older age and co-morbidity, and moderate but consistent evidence that symptom severity and lower educational level, all act as barriers of employment in people suffering from depression. All participants highlighted that the experience of depression and the consequences it might have for employment are entirely personal and may be experienced very differently by different people, despite having 6 Approximately 80 per cent of whom had a diagnosis of Unipolar Depression. The symptoms most often suggested by experts as problematic in terms of employment were low mood, lack of motivation/interest, difficulty concentrating, being easily distracted and negative thinking.
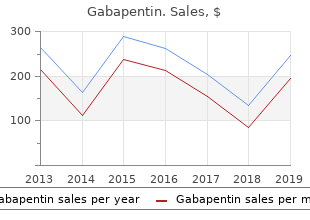
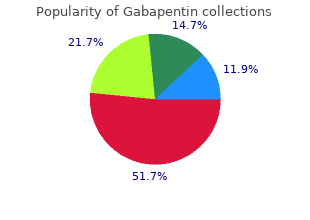
Soybean Curd (Soy). Gabapentin.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96936
Diseases
Adenomas are asymptomatic order cheap gabapentin on-line medications you can take while nursing, being detected on ultrasound or found incidentally at surgery buy gabapentin online pills symptoms 6 days before period. Small masses in the wall of the gallbladder discount gabapentin 300mg online symptoms yellow eyes, however, are relatively common findings on ultrasound; when multiple they usually First Principles of Gastroenterology and Hepatology A. Congenital Fibrocystic disorders: This group of disorders comprises biliary tree maldevelopment. Cystic dilatation and/or fibrosis are due to genetic abnormalities in the remodeling of the ductal plate. The later the presentation, the less significant is the renal component of the syndrome: 90% in perinatal vs. Carolis disease (congenital intrahepatic biliary dilation) is a rare condition in which saccular, dilated segments of the intrahepatic bile ducts can lead to stone formation, recurrent cholangitis and/or liver abscesses. Episodes of abdominal pain, fever and jaundice, most commonly occur in childhood or young adult life. Cholangiography reveals the irregularly dilated segments of the intrahepatic bile ducts that connect with the main ducts. Management is conservative, using antibiotics for infectious complications of the duct system. Endoscopy (or surgery) can remove some stones but does little for the process that affects small bile ducts in the liver. If involvement is unilateral (usually left-sided), partial hepatectomy can be curative. These recurrent episodes of cholangitis can rarely progress to secondary biliary cirrhosis, portal hypertension and eventually cholangiocarcinoma. Congenital hepatic fibrosis frequently accompanies Carolis disease; the combination is termed Carolis syndrome. This phenomenon perhaps reflects a developmental defect of the small interlobular ducts. Congenital hepatic fibrosis presents as portal hypertension with esophageal varices in children. Liver biopsy is diagnostic, revealing broad bands of fibrous tissue entrapping bile ducts. Choledochal cyst is an uncommon congenital dilation of a portion of the common bile duct that develops because of an uneven proliferation of the duct epithelial cells. More than 50% of cases are associated with an anomalous pancreaticobiliary junction, due to an arrest of the normal descent of this junction from outside the duodenum to within the duodenal wall in the last eight weeks of gestation. A long common pancreaticobiliary channel (> 15 mm) may allow pancreatic juice reflux in the bile duct, causing distal stricturing and thinning of the bile duct proximally, at least in some cases. Choledochal cysts have been classified into subtypes dependent upon site, most commonly as a fusiform dilatation of the extrahepatic bile duct, but also as a sidewall diverticulum or even bulging as a sac into the duodenum. Presentation may be as cholestasis in infants (if the cyst and/or stricture is complicated by sludge), as an abdominal mass, or rarely, as an acute abdomen if the cyst bursts and causes bile peritonitis. The cysts can be quite large: 2-8 cm in size and having up to 8 L of dark brown fluid. Later in life, they present as intermittent jaundice, biliary pain and cholangitis. Chronic obstruction rarely can lead to biliary cirrhosis and First Principles of Gastroenterology and Hepatology A. Because of the risk of malignancy, either related to the cyst itself or to the abnormal pancreaticobiliary junction, a radical excision with hepaticojejunostomy is preferred. This also helps reduce the postoperative risk of stricturing and stone formation when the bile duct is surgically attached to the intestine. Alagilles syndrome is a marked reduction in intrahepatic (actually interlobular) bile ducts. Although it is believed to be congenital, being inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, presentation may be as a neonatal jaundice or as cholestasis in older children. Outcome is variable, depending upon the attendant anomalies and the severity of the liver disease. Complete absence of the extrahepatic bile ducts reflects either an arrest in remodeling of the ductal plate in utero or, more probably, an inflammatory destruction of the formed bile ducts during the postpartum period. An initial viral injury may initiate the epithelial injury that then progresses by an immune-mediated sclerosing process, abetted by bile salt leakage that adds detergent damage. The resultant sclerosing inflammation obliterates both the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts, resulting in profound cholestasis and then secondary biliary cirrhosis. Chronic cholestasis then leads to steatorrhea, skin xanthomas, bone disease and failure to thrive. Surgery is usually necessary to confirm the diagnosis and attempt some form of biliary drainage. In some, existence of a patent hepatic duct or dilated hilar ducts allows correction of the obstruction by anastomosis to the small intestine (e. More common is an absence of patent ducts; dense fibrous tissue encases the perihilar area and precludes conventional surgery. Such obliteration of the proximal extrahepatic biliary system requires the Kasai procedure. A conduit for biliary drainage is fashioned by resecting the fibrous remnant of the biliary tree and anastomosing the porta hepatis to a roux-en-Y loop of jejunum. With either surgery, most children eventually develop chronic cholangitis, hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis and portal hypertension. When the child is larger, hepatic transplantation dramatically improves the prognosis. Liver transplantation becomes necessary in 50% by 2 years of age, 80% by 20 years. Other causes of neonatal cholestasis can be attributed to hepatocellular transport defects, best exemplified by familial intrahepatic cholestatic syndromes. These small, multiple cysts are usually asymptomatic though potentially complicated by cholangiocarcinoma. Cholangitis Cholangitis is any inflammatory process involving the bile ducts, but common usage implies a bacterial infection, usually above an obstructive site (usually a bile duct stone). The presence of bacteria in the biliary tree plus increased pressure within the system results in severe First Principles of Gastroenterology and Hepatology A. Any condition producing bile duct obstruction is likely to cause bacterial infection of bile. A less likely cause of infection is a stricture (such as a neoplasm) that has not been contaminated by a stent; only 10-15% of malignant biliary obstructions are associated with infection at presentation. The difference relates to the slowly progressive obstruction of non- contaminated strictures versus the intermittent blockage with a stone or acute blockage of as stent within a duct that has been colonized by bacteria via the stent.