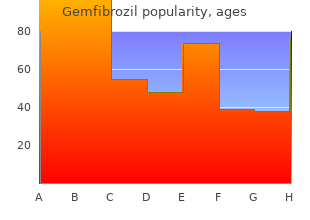


Bienville University. G. Sobota, MD: "Order Gemfibrozil online - Trusted Gemfibrozil".
Clients not only have the right to access but also buy gemfibrozil paypal cholesterol mg/dl, where appropriate order gemfibrozil 300mg line cholesterol chart levels uk, the right to rectification discount 300mg gemfibrozil cholesterol test alcohol. They may apply either through the courts or the Data Protection Commissioner to have any inaccurate data and opinions based on that data rectified or removed (Data Protection Act 1998). Sharing of health records with the client is recognised as good practice and is one way of involving them in the health care process. Retention of health records There are recommended minimum periods of retention for health records. Primary documents would include casenote folders, client identifica tion information, admission sheets, referral letters, case history sheets, as sessment or examination information, progress notes, operation sheets, nursing careplans, therapy notes, reports and anaesthetic sheets. THE LEGAL FRAMEWORK 41 Primary documents have to be retained for a legal minimum period (NHS Executive 1999): ° Maternity records must be kept for 25 years. In cases where a child has died before they are 18, the records must be retained for eight years after the death. The conclusion of treatment includes all follow-up checks and actions in connection with that treatment. Recommended minimum retention periods for GP records are similar ex cept for: ° Records relating to personnel serving in HM Armed Forces or persons serving a prison sentence are not to be destroyed (NHS Executive 1998). Secondary documents (for example x-rays and drug sheets) and transitory documents (for example blood pressure charts) are retained for periods of time determined by locally agreed policies. For instance, diaries, annual leave requests and job descriptions are just some of the documents covered by the regulations. Health professionals are responsible for the records they create and use, but the NHS Trust or health authority usually has ownership and copyright of these records. They should be told about their choice in deciding with whom information may be shared. These clinical notes are essential for ensuring the delivery of appropriate and effective care. They will contain information on investigations, diagnosis, care and intervention. A complete record will also include the views of the client and family in addition to those of the health professional. There will be an account of the client’s and the family’s understanding of and reaction to the present ing problem. It will also give a description of their wishes, responses to and participation in the delivery of care and treatment. Record keeping skills Health professionals are personally accountable for what they have written in health records. With the increase in litigation it is more important than ever that clinicians ensure that records are complete and comprehensive. For instance, records are one way that competent practice may be demon strated when a client has complained (Fisher 2001). Record keeping skills must therefore be seen as an essential clinical skill. The ability to record, interpret and disseminate written information about a client, like any other clinical skill, is essential. Record keeping skills must: ° form a fundamental component of pre-qualification training ° be considered part of professional development and undergo the same scrutiny as other clinical skills and knowledge 43 44 WRITING SKILLS IN PRACTICE ° be considered one of the essential elements of clinical practice and therefore be regularly reviewed by the reflective practitioner ° be included in clinical audit so that standards of recording are not only maintained but also areas for improvement are identified ° be regularly updated to take into account the rapid changes in information management and the introduction of new technologies. Advice is offered about record keeping by various professional bodies, and is often set down as standards to which members are expected to adhere. Employers also have a statutory duty under the Health Act (1999) to monitor and improve the quality of health care. This would include audit ing the standard of record keeping on a regular basis to ensure that the quality of information management is maintained (Dimond 2000). It is therefore essential that clinicians familiarise themselves with the requirements of both the association representing their particular disci pline and their employers. It is recognised as good practice to record every contact with the client. A direct contact means any face-to-face interaction with the client, such as carrying out a test or providing treatment. An indirect contact relates to any actions you carry out that are related to meeting the needs of a specific client. This might be liaison, advising family and carers or attending meetings such as case conferences. It would also in clude recording indirect contacts initiated by other professionals, for ex ample receiving a telephone call regarding one of your clients. It may be the case that not all of your planned contacts occur, for ex ample clients may fail to attend. For example, make a note of any attempts to liaise with other professionals even if you are unable to get in touch with them. This provides evidence of not only your intended actions for that client, but also the reasons why these may not have been fulfilled. It is also advis able to record the time, especially if you make a series of direct or indirect contacts with a specific client on the same day. This helps to show the de velopment of events, often a critical issue in litigation cases. Give the name of the location where the client was seen, for example on a home visit, as an out-patient or in the community clinic. A complete health record will provide the reader with all the information required to reach the same conclusions as the health professional who wrote the notes. The type and amount of information noted would be determined by the clinical need of the client, and the context in which the client is seen. For example, documenting an acute episode would vary from the on-going documentation required in a long-stay care facility. The position of the client along the care pathway will also have a bear ing on deciding the content of notes. The main stages in the health care process are: ° referral ° initial assessment ° intervention (including on-going evaluation) ° discharge ° post-discharge. The following sections offer guidance on the type of information to record at each stage of the care pathway. However, each clinician is reminded to refer to the standards and practices set down by his or her employing or ganisation and his or her professional body. Setting up a personal health record A personal health record is set up for the client either when a referral is re ceived by the service or at the first contact with the client. The Audit Com mission (1995), in a study of hospital records, found that there was no common approach to how these records were organised. They suggested that notes have a clear structure that is agreed with the users – that is, the health professionals and the administrative staff. This will help users in identifying the current epi sode and the most recent entry. Arranging data into specific sections like assessments, treatment and so on may also help the reader to quickly locate the relevant information. Every clinician has a responsibility to check, update and maintain the client records they are using.
Chemical mutagenesisCHEMICAL MUTAGENESIS Epstein (Martha Cowles Chase Epstein) order 300mg gemfibrozil overnight delivery cholesterol chart pdf, she later returned to Cleveland Heights purchase 300 mg gemfibrozil visa cholesterol check guidelines, Ohio generic gemfibrozil 300 mg line cholesterol levels triglycerides normal, where she lived with her father, The interaction of certain environmental chemical compounds Samuel W. After graduating from college, Chase worked and cell metabolism may result in genetic changes in DNA as an assistant to Alfred Hershey at the Carnegie Institution of structure, affecting one or more genes. Many ical period in the history of modern genetics and the beginning cancers and other degenerative diseases result from acquired of an entirely new phase of research that established the science genetic mutations due to environmental exposure, and not as of molecular biology. Including the name of an assistant or tech- an outcome of inherited traits. Chemicals capable of inducing nician on a publication, especially one that was certain to genetic mutation (i. Some of these natu- ral compounds may also be genotoxic for humans and ani- Autotrophic bacteria obtain the carbon that they need to sus- mals, when that plant is consumed frequently and in great tain survival and growth from carbon dioxide (CO2). For instance, most edible mushrooms contain a fam- process this carbon source, the bacteria require energy. That is, they derive their energy from the Among the most aggressive man-made chemical muta- energy already stored in chemical compounds. By oxidizing genes are: the compounds, the energy stored in chemical bonds can be • asbestos utilized in cellular processes. Examples of inorganic com- • DDT pounds that are used by these types of bacteria are sulfur, ammonium ion (NH4+), and ferrous iron (Fe2+). The designation • diesel and gasoline exhaust lithotrophic means “rock eating,” further attesting to the abil- • polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) ity of these bacteria to grow in seemingly inhospitable envi- Exposure to some of these compounds may occur in the ronments. For instance, insecticide and her- consists of large chemicals that are complex in structure, as is bicide sprayers on farms, tanners, and oil refinery workers are the case when the chemicals are derived from once-living organisms, then it is the chemoautotrophic bacteria that utilize frequently exposed to arsenic and may suffer mutations that the source. If the molecules are small, as with the elements lead to lung or skin cancers. Insulation and demolition work- listed above, they can be utilized by chemolithotrophs. Painters, dye users, furniture include bacteria, fungi, animals, and protozoa. People bacteria are distinct from the sulfur bacteria that utilize sun- working in the manufacture of wood products, paper, textiles light. The latter contain the compound chlorophyll, and so and metallurgy, as well as hospital and laboratory workers, are appear colored. Colorless sulfur bacteria oxidize hydrogen frequently in contact with formaldehyde and can thus suffer sulfide (H2S) by accepting an electron from the compound. Cigarette The acceptance of an electron by an oxygen atom creates and cigar smoke contains a class of chemical mutagenes, water and sulfur. The energy from this reaction is then used to known as PAH (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons), that leads reduce carbon dioxide to create carbohydrates. PAH is also present in gas and diesel a colorless sulfur bacteria is the genus Thiothrix. Except for the cases of accidental high exposure and These bacteria are most commonly encountered as the rusty contamination, most chemical mutagenes or their metabolites coloured and slimy layer that builds up on the inside of toilet (i. In a series of chemical reactions that is similar to those gradual accumulation in DNA, throughout years of exposi- of the sulfur bacteria, iron bacteria oxidize iron compounds tion. Some individuals are more susceptible to the effects of and use the energy gained from this reaction to drive the for- cumulative contamination than others. Examples of iron bacteria are degrees of susceptibility are due to discreet genetic varia- Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Thiobacillus thiooxidans. Chemoauto- morphic version of Cytochrome P450 genes, an individual trophs thrive in such an environment. A third type of chemoautotrophic bacteria includes the Polymorphism in another group of genes, NAT (N-acetyl- nitrifying bacteria. These chemoautotrophs oxidize ammonia transferase), is also implied in different individual suscepti- (NH3) to nitrate (NO3-). Plants can use the nitrate as a nutrient bilities to chemical exposure and mutagenesis. These nitrifying bacteria are important in the operation of the global nitrogen cycle. Examples of chemoautotrophic See also Immunogenetics; Mutants, enhanced tolerance or nitrifying bacteria include Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. For his work, Domagk received the 1939 recent years scientists have studied a cave near Lovell, Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. The groundwater running through the cave con- replaced by antibiotics, sulfa drugs are still commonly used tains a strong sulfuric acid. The against urinary tract infections, Hanson disease (leprosy), only source of life for the thriving bacterial populations that malaria, and for burn treatment. In 1928, the British bacteri- The energy yield from the use of inorganic compounds ologist Alexander Fleming noticed that a mold on an is not nearly as great as the energy that can be obtained by other uncovered laboratory dish of staphylococcus destroyed the types of bacteria. He identified the mold as Penicillium notatum, which do not usually face competition from other microorganisms, so was related to ordinary bread mold. Fleming named the mold’s the energy they are able to obtain is sufficient to sustain their active substance penicillin, but was unable to isolate it. Indeed, the inorganic processes associated with In 1939, the American microbiologist René Jules Dubos chemoautotrophs and chemolithotrophs may make these bacte- (1901–1982) isolated from a soil microorganism an antibacte- ria one of the most important sources of weathering and ero- rial substance that he named tyrothricin. These are bacteria that live in extremes of pH, antibiotic that was effective on gram-negative bacteria. Moreover, it has Isolating it from a Streptomyces fungus that he had studied been suggested that the metabolic capabilities of extremophiles for decades, Waksman named his antibiotic streptomycin. Though streptomycin occasionally resulted in unwanted side effects, it paved the way for the discovery of other antibiotics. See also Metabolism The first of the tetracyclines was discovered in 1948 by the American botanist Benjamin Minge Duggar. Working with Streptomyces aureofaciens at the Lederle division of the CHEMOSTAT AND TURBIDOSTAT • see American Cyanamid Co. LABORATORY TECHNIQUES IN MICROBIOLOGY The first effective chemotherapeutic agent against viruses was acyclovir, produced in the early 1950s by the American biochemists George Hitchings and Gertrude Belle CHEMOTAXIS • see BACTERIAL MOVEMENT Elion for the treatment of herpes. Today’s antiviral drugs are being used to inhibit the reproductive cycle of both DNA and RNA viruses. For example, two drugs are used against the CChemotherapyHEMOTHERAPY influenza A virus, Amantadine and Rimantadine, and the AIDS treatment drug AZT inhibits the reproduction of the human Chemotherapy is the treatment of a disease or condition with immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The first modern therapeutic cal compounds for use as cancer treatments as early as the chemical was derived from a synthetic dye. But the first effective treatments were drugs developed in the 1930s, penicillin and other antibiotics the sex hormones, first used in 1945, estrogens for prostate of the 1940s, hormones in the 1950s, and more recent drugs cancer and both estrogens and androgens to treat breast cancer.
Pulse generator and pacing wire Defibrillation and permanent pacemakers The sophisticated electronics contained in modern pulse generators may be damaged by the output from a defibrillator effective 300mg gemfibrozil cholesterol level in quail eggs, although a protection circuit contained in the generator helps to reduce this risk generic gemfibrozil 300 mg with mastercard cholesterol test in walgreen. Defibrillator electrodes should be placed as far as possible from a pacemaker generator discount gemfibrozil generic cholesterol and diabetes, but at least 12. Chest radiograph If the generator has been put in the usual position below showing the left clavicle, the conventional anterolateral position may be biventricular pacemaker with suitable. After successful resuscitation the device should be leads in the right checked to ensure that the programming has not been ventricle, right affected. This complication may not become apparent until some time after the shock has been given. For this reason the pacing threshold should be checked regularly for several weeks after successful resuscitation. The implantable cardioverter defibrillator The implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) was developed for the prevention of sudden cardiac death in patients with life- Defibrillation by an ICD threatening ventricular arrhythmias, particularly sustained VT or VF. Observational studies and recent prospective studies have shown their effectiveness. Technological advances have been rapid and modern cardioverter-defibrillators are much smaller than their predecessors. One or more electrodes are usually inserted transvenously, although a subcutaneous electrode is sometimes used. Some new designs use subcutaneous electrodes exclusively and are implanted over the heart; no transvenous or intracardiac electrodes are required. Currently available models feature several tachycardia zones with rate detection criteria and tiered therapy (low-energy cardioversion and high-energy defibrillation shocks) independently programmable for each zone. Extensive diagnostic features are available, including stored ECGs of the rhythm before and after tachycardia detection and treatment. Defibrillation is achieved by an electric charge applied Changes in ICDs over 10 years (1992–2002). Apart from reduction in size, between the anodal and cathodal electrodes. The site and the implant technique and required hardware have also improved—from the sternotomy approach with four leads and abdominal implantation to the number of anodes and cathodes, the shape of the shock present two-lead transvenous endocardial approach that is no more invasive waveform, and the timing and sequence of shocks can all be than a pacemaker requires pre-programmed. Biphasic shocks (in which the polarity of the shock waveform reverses during the discharge) are widely used. The capacitors are charged from an integral battery, which takes 5-30 seconds after the recognition of the arrhythmia. Implantable defibrillators incorporating an atrial lead are also available. These provide dual-chamber pacing and can also distinguish atrial from ventricular tachyarrhythmias. They are used in patients who require an ICD and concomitant dual- chamber pacing, and in patients with supraventricular Cardioversion of ventricular tachycardia by an ICD tachycardias that may lead to inappropriate ICD discharge. Atrial defibrillators have also become available in recent years to treat paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Abdominal insertion or thoracotomy (needed with earlier models) is rarely required because most devices are now placed in an infraclavicular position similar to that used for a Resuscitation in patients with an ICD pacemaker Should resuscitation be required in a patient with an ICD, basic life support should be carried out in the usual way. If defibrillation is attempted no substantial shock will be felt by the rescuer. If it is deemed necessary to turn the device off this may be accomplished by placing a magnet over the ICD. If external defibrillation is attempted the same precautions should be observed as for patients with pacemakers, placing the defibrillator electrodes as far from the unit as possible. If ICDs for secondary prevention resuscitation is successful the ICD should be completely re- ● Cardiac arrest due to VT or VF assessed to ensure that it has not been adversely affected by the ● Spontaneous VT causing syncope or significant shock from the external defibrillator. ICDs have been shown to be 85 ABC of Resuscitation effective in the prevention of sudden cardiac death in these ICDs for primary prevention patients and are, therefore, indicated as a “secondary” preventative measure. In clinical trials ICDs have been shown to ● Patients with severe impairment of ventricular function following MI be more effective than anti-arrhythmic drugs in this role. Similarly, Non sustained VT on 24 hour ECG monitoring ICDs should be routinely considered in patients with sustained Inductive VT on electrophysiological testing VT leading to syncope or other substantial haemodynamic Left ventricular dysfunction with an ejection fraction of less compromise, again unless a treatable cause is discovered. Implantation incuding: of an ICD may be indicated as a preventative measure if the left – long QT syndrome ventricular ejection fraction is less than 35% and they have – hypertrophic cardiomyopathy experienced an episode of sustained VT, even without syncope – bugada syndrome or cardiac arrest. It is also possible to identify patients who have not yet suffered a life-threatening arrhythmia yet remain at high risk of sudden cardiac death. The use of ICDs is justified as a The National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) published “primary” preventative measure in these patients. One guidance for the implantation of ICDs applicable to the United important group in this category comprises those patients with Kingdom in September 2000. These include recommendations severe impairment of ventricular function after MI who have for their use in patients who have been successfully resuscitated non-sustained VT on Holter monitoring and inducible VT on from cardiac arrest or who have sustained life-threatening electrophysiological testing. These include structural disorders of cardiac muscle as well as physiological disorders involving abnormal ion transport mechanisms in the cell membrane. The results of the MADIT II trial are likely to widen the indications for the prophylactic use of ICDs. London: BMJ Publishing 30% reduction in mortality was observed in post-MI patients with Group, 2004. The ICDs from 1992 and 2002 were supplied by C D impaired left ventricular function randomised to receive an ICD Finlay, CRT coordinator, Guidant Canada Corporation, Toronto Further reading ● American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association. Guidance on the use Guidelines for the implantation of cardiac pacemakers and of implantable cardioverter defibrillators for arrhythmias. Implantable devices for ventricular ● Klein H, Auricchio A, Reek S, Geller C. In: Julian DG, Camm AJ, trials of sudden cardiac death in patients with left ventricular Fox KM, Hall RJC, Poole-Wilson PA, eds. A great deal has been written about the risk of contact of healthcare workers, rescuers, first aiders, and the general public with blood or body fluids of patients being resuscitated who are considered to be possible carriers of blood borne viruses (BBVs). The potential risks of infection to the rescuer are from two sources: airway management (airway and breathing) and needlestick injuries (circulation). Although BBVs are the greatest potential risk to rescuers, other non-viral organisms can pose a threat (tuberculosis and meningococcus). If mouth-to-mouth ventilation is performed on a patient with open tuberculosis then the rescuer is at risk. Follow up in a chest clinic, including checking BCG status, will Sharps box be necessary. Contact with droplet spray from a patient infected with meningococcal disease will require the rescuer to receive prophylactic antibiotics. Guidelines A report from the Centers for Disease Control has emphasised Risk from needlestick injuries that blood is the single most important source of human ● Transmission of BBVs immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and hepatitis B (HBV) and C HBV (HCV) viruses through the parenteral, mucous membrane, or HCV non-intact skin exposure.
Purchase 300 mg gemfibrozil with mastercard. 8 Herbs and Spices to Manage DIABETES: Simple but Effective Home Remedies You Should TRY.
Diseases