

University of Northern Iowa. Y. Cronos, MD: "Purchase Antivert online no RX - Proven Antivert online no RX".
Effects of varying the monetary value of voucher-based incentives on abstinence achieved during and following treatment among cocaine-dependent outpatients 25mg antivert everlast my medicine. Contingent reinforcement increases cocaine abstinence during outpatient treatment and 1 year of follow-up antivert 25mg low cost medications medicaid covers. Person- environment interaction in the prediction of alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence in adulthood best purchase antivert medications given during dialysis. Efficacy does not necessarily translate to cost effectiveness: A case study in the challenges associated with 21st-century cancer drug pricing. Young adults at risk for excess alcohol consumption are often not asked or counseled about drinking alcohol. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention. Days to treatment and early retention among patients in treatment for alcohol and drug disorders. Combat duty in Iraq and Afghanistan, mental health problems, and barriers to care. An action plan for behavioral health workforce development: A framework for discussion. Department of Health and Human Services, Annapolis Coalition on the Behavioral Health Workforce. Cost benefits of substance abuse treatment: An overview of results from alcohol and drug abuse. A genome-wide scan for loci influencing adolescent cannabis dependence symptoms: Evidence for linkage on chromosomes 3 and 9. The impact of Not on Tobacco on teen smoking cessation: End-of-program evaluation results, 1998 to 2003. Reliability of substance use disorder diagnoses among African-Americans and Caucasians. Long-term outcomes among drug-dependent mothers treated in women-only versus mixed-gender programs. Substance use and dependence education in predoctoral dental curricula: Results of a survey of U. Combining behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation: An update. Methodology, psychosocial treatment, selected treatment topics, research priorities (pp. Brief intervention, treatment, and recovery support services for Americans who have substance abuse disorders: An overview of policy in the Obama administration. A policy-oriented review of strategies for improving the outcomes of services for substance use disorder patients. Alcohol problems among emergency department patients: Proceedings of a research conference on identification and intervention. Nicotine dependence treatment during inpatient treatment for other addictions: A prospective intervention trial. Contingency management in methadone maintenance: Effects of reinforcing and aversive consequences on illicit polydrug use. Five-year outcomes of therapeutic community treatment of drug-involved offenders after release from prison. Institute of Medicine, Committee on Crossing the Quality Chasm: Adaptation to Mental Health and Addictive Disorder. Improving the quality of health care for mental and substance-use conditions: Quality chasm series. Dispelling the myths about addiction: Strategies to increase understanding and strengthen research. Gulf war and health: Physiologic, psychologic, and psychosocial effects of deployment-related stress (Vols. Returning home from Iraq and Afghanistan: Preliminary assessment of readjustment needs of veterans, service members, and their families. Alcohol use and alcohol-related problems before and after military combat deployment. Racial disparities in completion rates from publicly funded alcohol treatment: Economic resources explain more than demographics and addiction severity. White matter integrity in adolescents with histories of marijuana use and binge drinking. An examination of main and interactive effects of substance abuse recovery housing on multiple indicators of adjustment. The impact of stressful life events and social support on drinking among older adults: A general population survey. Comparative effectiveness of three approaches to serving people with severe mental illness and substance abuse disorders. A profile of alcohol and prescription drug abuse in a high-risk community-based elderly population. Evaluation of school-based smoking-cessation interventions for self-described adolescent smokers. Progress in the development of topiramate for treating alcohol dependence: From a hypothesis to a proof-of-concept study. Update on neuropharmacological treatments for alcoholism: Scientific basis and clinical findings. Dose-ranging kinetics and behavioral pharmacology of naltrexone and acamprosate, both alone and combined, in alcohol-dependent subjects. Association between cigarette smoking and anxiety disorders during adolescence and early adulthood. An update on state budget cuts: At least 46 states have imposed cuts that hurt vulnerable residents and cause job loss. A comparison of levomethadyl acetate, buprenorphine, and methadone for opioid dependence. Rewarding results: Improving the quality of treatment for people with alcohol and drug problems. Standards for behavioral health care: Standards elements of performance scoring accreditation policies. Confirming the effectiveness of an evidence-based practice: Use of motivational interviewing in the real world. In Central East Addiction Technology, An overview of evidence-based practices: Implementing science-based interventions in practical settings (pp. In Central East Addiction Technology, An overview of evidence-based practices: Implementing science-based interventions in practical settings (pp.
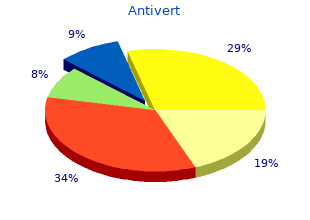
Lungwort. Antivert.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96248
Prophylaxis for steroid induced mania has taken the form of lithium or low dose neuroleptics trusted 25 mg antivert medications lexapro. Glatiramer acetate is another disease-modifying drug with modest effects discount antivert 25mg visa medicine administration, with a substantial minority of cases showing a less than optimal response order antivert 25mg on line medicine 751. Immunosuppression with drugs such as azathioprine and methotrexate may be needed for the most progressive cases. Mitoxantrone is a chemotherapeutic drug for non-responsive cases which may cause cardiomyopathy or acute leukaemia. Air encephalography revealed enlarged ventricles and increased air collection over the hemispheres. Alternatively there are high-density areas enhancing with contrast during an acute relapse. When testing visual evoked responses it is normal to get a major downward (positive) wave at about 100-msec (P100). Demyelination of the optic nerve delays this wave with relative preservation of its form. Depression appears to be predicted by multiple interacting variables, especially trait anxiety and functional status but also alexithymia and level of satisfaction with social support system. Amantadine or modafinil may 2969 improve fatigue; other approaches include aerobics, rest periods, and heat avoidance. There is some evidence that oral cannabinoids may also be useful for spasticity (Zajicek ea) but they should only be employed if legal, available, if other treatments do not work, and if the patients desists from driving. Many of the changes of senility 2971 develop and the end state is eventually reached. Lamin A 2972 (progerin) truncation has been reported (De Sandre-Giovannoli ea, 2003) causing nuclear membrane disruption and altered transcription. Cysts of the third ventricle Colloid cysts are usually silent until the third to fifth decades of life. They may cause delusional depression, delirium, dementia, neurotic syndromes, and schizophrenia-like psychosis. Lamin A is part of the protein network forming the nuclear lamina inside the nuclear membrane. Cystic tumours can be aspirated, which may reverse mutism, although the patient will be unable to remember anything for the time when mute. There is often a family history of the disorder, with autosomal recessive transmission in childhood-onset cases. Other reported neurological effects were dysexecutive syndrome, memory problems, periods of confusion, dementia, psychosis (bipolar or schizoaffective), and dural sinus thrombosis. Neurological effects include peripheral neuropathy, encephalopathy, cerebral/subarachnoid haemorrhage, damage to cranial nerves, a mass effect from necrotic brain tissue, and delirium. Score Score (1) Orientation What is the year/season/date/day/ females and with increasing longevity. The total can be brought up to 40 points by adding tests that mainly test right hemisphere function: (1) Draw a triangle, square and circle, or construct three shapes with matches (3 points). They become distracted by accidental impressions/events and cannot shift attention away from them. Wise and Strub (1999) point out that the examiner should not only ask patients to remember 3 objects (verbal/dominant) but they should also ask them to recall 3 shapes (non-dominant hemisphere). This brief test with a deep floor (taps low levels of function) employs a screening approach: moderately difficult items are presented first, allowing other items in that domain to be skipped if the patient passes. Thyroid screening may be misleading in people on phenothiazines, antiparkinsonian drugs, or lithium. Polycythaemia occurs in multi-infarct dementia and haemangioblastoma of the cerebellum. Presenile dementia slows down most of the components of the visual evoked response. Epilepsy 2997 Epilepsy , a seizure tendency symptomatic of a brain affectation, follows a chronic course with repeated, unprovoked seizures. International League Against Epilepsy definitions Epileptic seizure = clinical manifestation thought to be due to an abnormal and excessive discharge of a set of brain neurones Epilepsy = disorder with at least 2 epileptic seizures that are unprovoked by an immediate identifiable cause 2998 Rarely if ever is the cause of epilepsy centrencephalic. Pseudoseizures (non-epileptic attack disorder or non-organic/non-epileptic 2999 seizures ) are not discussed here except to state that the ultimate diagnostic procedure is videotelemetry. Pseudoseizures must be distinguished from self-induced seizures, usually associated with childhood, wherein a person with epilepsy deliberately sets about inducing a seizure, e. A wide range of figures for relapse rates are to be found in different studies of people who 3002 have had a single seizure. Methohexitone can assist, especially when used with sphenoidal electrodes, to localise interictal spikes. Precipitants of epilepsy include laughing (gelastic - Gk, gelastikos, to laugh), startle, flickering light (photic), reading, fatigue, hunger, eating (Abenson, 1969), dehydration (including a hot bath), fever, and rare individual precipitants such as remembering a specific event or a particular body movement. Other precipitants of epilepsy include lack 3006 of sleep, emotional stress, infection, and alcohol or drug ingestion or withdrawal. Epileptic psychoses 3007 (a) with disturbed consciousness 3001 It was suggested by Brainwave Ireland (founded 1967; 353+(0)1+4557500; 249 Crumlin Road, Dublin 12; info@epilepsy. Risk of recurrence is three times higher for someone who is less age 50 years, who has a family history of febrile fits or seizures of any kind, and whose first fit occurs between midnight and 8 a. Such laughter is unlike normal laughter and is not usually viewed as being funny by an observer. Hamartoma of the hypothalamus may cause gelastic seizures as well as precocious puberty and aggressiveness; most cases are cognitively impaired, although at least some of this may be due to the seizures or their treatment. If the patient cries during laughter the term dyscrastic seizure (Gk, dyskrasia, bad mixture) may be employed. A prodrome is more frequently encountered with localisation-related epilepsy but it may be seen with generalised epilepsy. Ictal disorders of psychiatric importance include aura, automatism, and non-convulsive status epilepticus. The aura (a simple partial seizure) consists of premonitory symptoms of focal origin and lasts a matter of seconds. Other symptoms include vertigo, tinnitus, odd or indescribable feelings in various body parts such as head (cephalic aura), genitals, special sense changes, intense emotion, micropsia/macropsia, déjà vu, jamais vu, depersonalisation, and a variety of complex hallucinations. Most automatisms occur during a seizure or during post-ictal delirium but some patients with simple partial seizures have such phenomena (e. Postictal states may last 1-2 minutes and may consist, for example, of confusion (delirium), fugue, twilight state, or aggressiveness. Post-ictal psychoses commence after a short post-ictal lucid interval and resolve within a few days; they are the commonest of the epilepsy-associated psychoses; they are abrupt in onset; affective symptoms (especially agitation) accompany the psychosis; and a minority (15% after 15 years) go on to develop chronic interictal psychosis, especially those with severe seizures and structural change. Factors that may feed into postictal states Psychosocial (stigma) Early onset epilepsy (failure of fits to remit, frequent seizures, male sex, or left-sided lesions) Temporal lobe (especially bilateral) and other focal lesions Poor seizure control Genetic predisposition to epilepsy or psychiatric disorder or both Intellectual disability Acquired brain conditions like trauma Drugs (anticonvulsants, other drugs, and alcohol) 3009 Polypharmacy According to Lambert ea,(2003, p. Inter-ictal symptoms/disorders have been classified into mood (anxiety and/or depression – the commonest epilepsy-associated psychiatric problems), schizophrenia-like, behavioural/personality- 3010 related , and dementia. Earlier onset of interictal psychosis may be associated with generalised epilepsy, normal intellectual functioning and a family history of psychosis.
Rosa pomifera (Rose Hip). Antivert.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96814
Either kidney function is impaired by the use of diuretics buy antivert in united states online treatment quinsy, or the kidney is lacking necessary hormonal stimulation buy cheap antivert on line medications used to treat bipolar, as in adrenal insufficiency buy 25mg antivert visa symptoms jock itch, or there is a primary renal problem, such as tubular damage from acute tubular necrosis. When patients are hypovolemic, treatment of the hyponatremia requires correction of the volume status, usually replacement with isotonic (0. It commonly occurs as a result of congestive heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, or the nephrotic syndrome. Renal failure itself can lead to hypotonic hyponatremia because of an inability to excrete dilute urine. In any of these cases, the usual initial treatment of hyponatremia is administration of diuretics to reduce excess salt and water. Thus, hypovolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia is often apparent clinically and often does not present a diagnostic challenge. Euvolemic hyponatremia, however, is a frequent problem that is not so easily diagnosed. This measurement is taken to determine whether the kidney is actually capa- ble of excreting the free water normally (osmolality should be maximally dilute, <100 mOsm/kg in the face of hyposmolality or excess free water) or whether the free water excretion is impaired (urine not maximally concen- trated, >150-200 mOsm/kg). If the urine is maximally dilute, it is handling free water normally but its capacity for excretion has been overwhelmed, as in central polydipsia. More commonly, free water excretion is impaired and the urine is not maximally dilute as it should be. Two important diagnoses must be considered at this point: hypothyroidism and adrenal insufficiency. Thyroid hormone and cortisol both are permissive for free water excretion, so their deficiency causes water retention. In contrast, patients with Addison disease also lack aldos- terone, so they have impaired ability to retain sodium. Patients with adrenal insufficiency are usually hypovolemic and often present in shock. Because of retention of free water, patients actually have mild (although clinically inap- parent) volume expansion. Additionally, if they have a normal dietary sodium intake, the kidneys do not retain sodium avidly. Therefore, modest natriuresis occurs so that the urine sodium level is elevated to more than 20 mmol/L. Patients with severe neurologic symptoms, such as seizures or coma, require rapid partial correction of the sodium level. When there is concern that the saline infusion might cause volume overload, the infusion can be administered with a loop diuretic such as furosemide. The diuretic will cause the excretion of hypotonic urine that is essentially “half-normal saline,” so a greater portion of sodium than water will be retained, helping to correct the serum sodium level. When hyponatremia occurs for any reason, especially when it occurs slowly, the brain adapts to prevent cerebral edema. Solutes leave the intra- cellular compartment of the brain over hours to days, so patients may have few neurologic symptoms despite very low serum sodium levels. If the serum sodium level is corrected rapidly, the brain does not have time to readjust, and it may shrink rapidly as it loses fluid to the extracellular space. It is believed that this rapid shrinkage may trigger demyelination of the cerebellar and pontine neurons. Demyelination can occur even when fluid restric- tion is the treatment used to correct the serum sodium level. Therefore, sev- eral expert authors have published formulas and guidelines for the slow and judicious correction of hyponatremia, but the general rule is not to correct the serum sodium concentration faster than 0. His serum sodium level is initially 116 mEq/L and is corrected to 120 mEq/L over the next 3 hours with hypertonic saline. He has never had any health problems, but he has smoked a pack of cigarettes per day for about 35 years. His physical examination is notable for a low to normal blood pressure, skin hyperpigmentation, and digital clubbing. You tell him you are not sure of the problem as yet, but you will draw some blood tests and schedule him for follow-up in 1 week. The labo- ratory calls that night and informs you that the patient’s sodium level is 126 mEq/L, potassium level is 6. Which of the following is the likely cause of his hyponatremia given his presentation? Her medical history is remarkable only for hypertension, which is well controlled with hydrochlorothiazide. Her examination and laboratory tests show no signs of infection, but her serum sodium level is 119 mEq/L, and plasma osmolarity is 245 mOsm/kg. On the first postoperative day, he is noted to have significant hypona- tremia with a sodium level of 128 mEq/L. You suspect that the hypona- tremia is due to the intravenous infusion of hypotonic solution. In the postoperative state or in situations where the patient is in pain, the serum vasopressin level may rise, leading to inappropriate retention of free water, which leads to dilution of the serum. Hyponatremia in the setting of hyperkalemia and acidosis is sus- picious for adrenal insufficiency. This patient’s examination is also suggestive of the diagnosis, given his complaints of fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, and hyperpigmentation. The underlying cause of the adrenal gland destruction in this patient probably is either tuberculosis or malignancy. Because the patient is hypovolemic, probably as a result of the use of diuretics, volume replacement with isotonic saline is the best ini- tial therapy. Hyponatremia caused by thiazide diuretics can occur by several mechanisms, including volume depletion. In a patient with hyponatremia due to the infusion of excessive hypotonic solution, the serum osmolality should be low. The kidneys in responding normally should attempt to retain sodium and excrete water; hence, the urine sodium concentration should be low, and the urine osmolality should be low. When the infusion of hypotonic solution is used, the serum potassium level will also be low. This is in contrast to a situation of mineralocorticoid deficiency in which the sodium level will be decreased and potassium level may be elevated. Similarly, hyperaldosteronism can lead to hypertension and hypokalemia (Conn syndrome). Clinical Pearls ➤ Hyponatremia almost always occurs by impairment of free water excretion. Criteria include euvolemic patient, serum hypoosmolarity, urine that is not maximally dilute (osmolality >150-200 mmol/L), urine sodium more than 20 mmol/L, and normal adrenal and thyroid function.