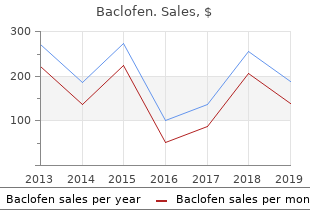


Regis College. Z. Dargoth, MD: "Order cheap Baclofen online no RX - Trusted Baclofen online".
It contributes to more deaths than alcohol and illicit drugs together order baclofen in united states online spasms body, and costs the economies of these countries millions of dollars a year 25mg baclofen mastercard muscle relaxant methocarbamol addiction. There is no doubt that the babies of mothers who smoke are smaller (by 200 g on average) than those of non- smoking mothers purchase 10 mg baclofen free shipping muscle relaxant pills over the counter. The smoking by the mother appears to reduce their resistance to disease, in particular to infection, so that babies born to smoking mothers die in infancy more often than average. By inhaling the smoke from either of their parents, these infants have more colds, bronchitis and other respiratory problems than babies in non-smoking homes. Any woman who smokes should ideally cease before she falls pregnant, but certainly should do so when the pregnancy is diagnosed. This is far easier said than done, but if her partner stops at the same time, support and encouragement is given by family and friends, and assistance is obtained from the family doctor, women who are motivated to give their baby the best possible chance in life will succeed in kicking this very addictive habit. The patient remains awake, but is often sedated, while an anaesthetist or surgeon places a needle into the lower back. The needle is inserted between the vertebrae so that the tip enters the spinal canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid and surrounds the spinal cord. The spinal cord carries all the nerve messages to and from the brain, and runs through the centre of the 24 vertebrae that form the backbone. A small amount of anaesthetic is injected into the spinal canal, so that the nerves below the level of injection no longer work and pain from the operation cannot be felt. The patient is often tilted slightly to prevent the anaesthetic from flowing further up the spine and affecting nerves above the level required for adequate anaesthesia. The side effects of a spinal anaesthetic include low blood pressure, a headache for several days, and a slow heart rate. This type of anaesthetic is usually given when the patient is not well enough to stand a general anaesthetic, for Caesarean sections, and in other circumstances when it is desirable for the patient to be awake. They are caused by a break down and stretching of the elastic fibres in the skin by changes in the body’s hormone levels as well as direct stretching of the skin. Once they form they usually remain permanently unless removed by plastic surgery or reduced by creams containing retinoic acids. Cushing syndrome is caused by an over production of steroids such as cortisone in the body, or taking large doses of cortisone. Headache, obesity, thirst, easy bruising, impotence, menstrual period irregularities, stretch marks, acne, high blood pressure, bone pain and muscle weakness are common symptoms of this syndrome. The most dangerous stage for the action of a teratogen is from three to twelve weeks of pregnancy. The eggs pass out in the faeces of the animal and may then enter a human mouth (eg. Once in the gut, the microscopic egg hatches and multiplies into millions of single-celled animals. In many patients, the symptoms are so mild that they are ignored, but in severe cases the patient complains of a low-grade fever, tiredness, muscle aches, joint pains, headache, sore throat, a mild rash and enlarged glands. If symptoms are significant or complications develop, medications are available. The infection may cause miscarriages, still birth, and deformities in the baby (eg. The disease can be detected by a specific immunoglobulin blood test, and this test is often routinely performed during antenatal blood examinations. If toxoplasmosis is detected in pregnancy, treatment will be given to cure the disease. Unfortunately, because the disease has already occurred, there may still be some damage to the foetus. During the first trimester (the first three months) the structure and form of the foetus are developed. The second trimester is involved with the growth of the foetus while the third trimester is the maturity of the foetus. A baby born at any time in the third trimester has a chance of survival, but the later the better. This allows a woman to attempt a natural vaginal delivery while a medical team is readily available to intervene with forceps or surgery if necessary for the health of the mother or baby. It is located in the pelvis and is loosely tethered to the pelvic walls by two ligaments on each side, the round and broad ligaments, giving it a high degree of mobility. The upper part of the uterus is called the body, and is attached to the two egg-conducting Fallopian tubes. It narrows at the lower end to form the cervix, or neck, which protrudes into the vagina and provides a passage for sperm to enter and menstrual blood to flow out. In the middle is a thick layer of muscle called the myometrium, while the inner lining consists of a blood enriched mucous membrane called the endometrium. Each month the endometrium thickens to prepare for the implantation of a fertilised egg. If this does not eventuate, all but the deepest part of the endometrium is discarded, leading to the monthly menstrual period. The menstrual flow consists of the liquefied dead endometrium together with some blood lost in the process. They expand to accommodate the growing foetus, and when the time comes for the baby to be born they engage in a series of contractions, helping the hitherto tightly closed cervix to open and propelling the baby into the vagina during labour. About six weeks after pregnancy, the muscles have shrunk again and the uterus has returned to its normal size. It is the passage into which the male penis is inserted during sexual intercourse. Vaginal secretions are released during sexual arousal and it can expand to facilitate intercourse. Sperm ejaculated during intercourse travel through the cervix and into the uterus and Fallopian tubes to fertilise an egg if one has been released. The lining of the vaginal wall is made up of a moist mucous membrane arranged in folds, which enable its muscular tissue to expand for the purposes of sexual intercourse and childbirth. The muscles in the wall of the vagina will also contract in spasms when a woman has an orgasm during intercourse. This rhythmic contraction aids the movement of the ejaculated sperm towards the cervix and uterus. In children the external opening to the vagina is partly covered by a thin mucous membrane called the hymen. This will be broken at the time of first sexual intercourse, or it may break spontaneously earlier than this. The tube leads to a suction device, which can create a vacuum, and the chain is attached to a handle that is held by the doctor.
It should also include support for individuals who are coping with the long- “Community involvement recognizes the term complications of diabetes cheap baclofen online amex back spasms 6 weeks pregnant. People with diabetes should be included in health care planning when it involves diabetes and health care delivery in their community best buy for baclofen muscle relaxant prescriptions. These people need to be supported by adequate training purchase 10mg baclofen with visa muscle relaxant id, access to resources and attention to the balance of physical and mental well-being in their jobs. Theresa Point Band Office the public, were convened across the Steinbach province during the spring of 1998 as an Bethesda Personal Care Home integral component of the Strategy. A the Pas Steering Committee and Secretariat member Cree Nation Tribal Health Centre were present to provide background to the the Pas Kikiwak Inn Manitoba Diabetes Strategy and identify the Thompson purpose of the public meeting. The format Keewatin Tribal Council Board Room for each meeting varied depending upon Thompson the site and the number of participants. Lions Centre Participants were asked to provide input Winnipeg Franco-Manitoban Cultural Centre regarding their issues, concerns and Winnipeg possible actions related to diabetes Freight House prevention, education, care, research and Winnipeg support. Lions Place the following community consultation sites the following sites were scheduled for the were convened by the Steering Committee: consultation process, but meetings were Arborg not held due to travel weather conditions, Town of Arborg Board Room or other logistical issues: Brandon Churchill Canadian Diabetes Association offices Lac Brochet Dauphin Thunders Restaurant Souris. School summarizing input received from health programs were frequently identified participants at the public meetings, relative as needing more emphasis on nutrition. Three hundred and improved labeling of food products could four people attended the sessions: 231 contribute to healthy eating by identifying members of the general public and 73 appropriate food choices. Site-specific records recommended that restaurants should play have been retained by the Strategy Steering a role in identifying healthy food Committee. Standards for school lunch Prevention programs were recommended in urban and There was general recognition of the need rural settings. Improved food choices in for prevention, heightened by the knowledge public arenas received comment in one that diabetes was increasingly a cause of northern setting. Concerns regarding the increased facilities was identified in rural and First rate of diabetes in children of First Nations Nations communities. It was stated programming in schools was identified as that governments need to identify needing attention in the context of prevention as a priority. Daily physical of health were also identified as important activity in schools was advocated. Incentive programs were Education recommended for the promotion of the need for more education of the preventive measures. There was concern the most frequent recommendation in expressed in both rural and First Nations northern and First Nations communities was consultations that individuals tend to the need to ensure the availability and develop a fatalistic approach once dia- affordability of appropriate foods. Education was seen as Nations communities made frequent a mechanism for generating hope and reference to the importance of traditional improved self-care. There was a strong foods in the prevention of diabetes and presentation regarding the need for the need to examine hunting regulations attention to literacy levels in the and the impact of such regulations on the development of a public education availability of traditional foods. Rural communities emphasized development of community gardens was the value of “wellness fairs” for public 72 Diabetes A Manitoba Strategy Public Meetings education, in addition to the usual media It was recommended that people living with methods of education. The need for diabetes should receive specific education general public education in traditional about the current standards of diabetes languages was advocated by Aboriginal care. In all sectors of the province, the Issues regarding traditional healing were school health curricula was identified as addressed in First Nations consultations. It was It was recommended that health clearly stated that health professionals need professionals receive education about current information. Specifically, there was traditional healing to promote an interface dismay expressed regarding the knowledge between Western and traditional approaches base of general and family practitioners. Enhanced education for physicians was There was a recommendation that recommended at a majority of public education must also be available in French meetings. The important role of family for individuals with diabetes and their physicians in diabetes care was stressed. The need for increased emphasis on dia- Care betes in nursing education programs was Issues of access to care were essentially identified in one consultation. General concerns included funding meet the education needs of First Nations for travel from rural and northern areas. Pharmacists were urban centres, access was identified as a identified as important in the education of concern for seniors, individuals with individuals with diabetes, providing that disabilities and individuals confined to pharmacists had increased education home. Access to education for about the availability of health professionals rural health workers was stressed in one in communities. The role of was frequently identified in northern and traditional healers was recommended as rural settings, with the exception of western requiring greater interface with Western areas of the province where availability of medical care programs. It was also ophthalmology and optometry was recommended that traditional foods be commended. There was almost universal demand for the the importance of client participation in development of diabetes screening care strategies was stressed in one programs. The cost of diabetes care supplies was seen Research as a barrier to optimal self-care in a majority Issues regarding research were less of public meetings. Recommendations frequently expressed than other elements of included review of taxation allowances for this Strategy. It was advocated that the medical expense claims and a need to scope of research needs to be broadened review Pharmacare costs. There was a recommendation contributing factor to the loss of interest in to increase the focus on research related to self-care. There was a stated desire to receive more It was recommended that nurses should information about funding levels for have an increased role in the provision of research in Manitoba and current research 74 Diabetes A Manitoba Strategy Public Meetings activities. First Nations consultations actions were as follows: specifically identified the importance of support groups in enhancing cultural Regarding education, it was recommended identity. There was a stated need to return that children are invaluable in educating to the historical cultural pattern of peers and the public regarding their illness “community caring. It was stated that access must clearly articulated that educators must be free of financial barriers. It viewed as being limited by the general lack was suggested that compulsory health of awareness of support programs among education of teachers should be considered health professionals. There were Availability of support programs was anecdotes of the difficulties faced in discussed. The scarcity of support groups in convincing school boards and school Winnipeg was identified as a concern and administrators of this issue. It was recommended care in schools for children with Type 1 dia- that there be improved supports for betes were identified as a concern. The regarding the integration of Type 1 and level of provincial government funding was Type 2 diabetes in a single provincial questioned. It was stated that the level of Strategy; it was felt that failure to clearly health care research funding should be differentiate Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes maintained even without a critical mass of issues and actions could become a researchers in Manitoba; in other words, disservice to the concerns of both diseases. There were specific concerns regarding the ethics of funding; anecdotal evidence suggested that funding dedicated to diabetes research was being applied to initiatives in other chronic diseases. Reallocation of funding from care to research was thought to be an issue for consideration, given the large amounts spent on care versus small amounts on research. Regarding support, it was emphatically stated that there was a need for greater recognition of the emotional and financial burden imposed upon children and their families by this life-long illness.
Most research and discrimination of people with diabetes purchase 10mg baclofen muscle relaxant half-life, programs are based on individual health as ensuring access to care and services and opposed to population health purchase generic baclofen on-line spasms under rib cage. Branch baclofen 25mg with amex spasms in intestines, which provides national the Canadian Diabetes Advisory Board leadership in policy development, health sponsored a workshop in October of 1994 research and system enhancement to to develop strategies to address the issues preserve and improve the health and related to diabetes in Canada. More • 3rd International Conference on Diabetes than 170 key stakeholders, including and Indigenous Peoples: Theory, Reality, consumers, healthcare professionals, Hope, May 26-30, 1995, Winnipeg, business leaders and government Canada. The delegates Association was established in 1995 came together to identify priorities, develop after the 3rd International Conference on action plans and discuss strategies to build Diabetes and Indigenous Peoples in an effective and efficient national model of Winnipeg, Manitoba. Some national and • the National Aboriginal Diabetes Strategy international initiatives to address this issue Discussion Paper, co-ordinated by the include: Medical Services Branch of Health Canada. The Southern Aboriginal Diabetes Initiative is a service developed to improve quality of care to Aboriginal people living with diabetes in southern Ontario. Refers to all Aboriginal groups including ownership of decision-making and resources as these Status, Non-Status First Nation people, Metis and pertain to its own betterment. This process is performed externally, either that provides health and social services on an through the blood (hemodialysis) or through the ambulatory and outreach basis using multi-disciplinary delicate linings inside the abdomen (peritoneal teams of health care providers and volunteers. The term “incidence” is sometimes used to children of a household head who has not denote incidence rate. Manitoba Health makes this determination for adults based on self-report of an individual (typically at the time when Manitoba Health numbers are issued). In the case of dependent children, this determination is automatically made for any children in a household when the household-head has made a declaration of entitlement under “The Indian Act” for themselves, or their children. The description “status” has been adopted to denote this population, although this specific phrase is not defined by “The Indian Act. Occurs most often in children, previously called Juvenile Diabetes and Insulin-Dependent dia- betes. Occurs most often in adults, previously called Maturity-Onset Diabetes and Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes. This form of dia- betes can be controlled with a combination of lifestyle changes, pills and/or insulin. Evaluation of a structured treatment and teaching programme on non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Epidemiology Unit & Diabetes and Chronic for the management of diabetes in Canada. A Planning Framework to of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Promote, Preserve and Protect the Health of Control and Prevention. Shared care for diabetes: A Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of systematic review. Indian and Northern Health Services - Medical Services Branch - Department of National Health and 38. Efficacy Welfare, First Nations’ Health Commission - Assembly of atenolol and captopril in reducing the risk of of First Nations, Canadian Diabetes Association. The Kahnawake Schools Diabetes Prevention Project: Intervention, Evaluation, and Baseline Results of a Diabetes Primary Prevention Program with a Native Community in Canada. Greg Nyomba Executive Director Assistant Professor of Medicine Health Action Centre Dr. Marilyn Tanner-Spence Department of Northern Affairs Nurse Epidemiologist Government of Manitoba Dr. Linda Williams Burntwood Regional Health Authority Inc Acting Zone Nursing Officer Koop, Ms. Morna Cook Unit Consultant Canada Prenatal Nutrition Program Pharmacy Consultant Diabetes and Chronic Diseases Unit Healthy Start for Mom and Me Canadian Diabetes Association Public Health Branch, Manitoba Health Wylie, Ms. Kevin External Programs & Operations Division Executive Director Chief Executive Officer Watts, Ms. Sandy Interlake Regional Health Authority Inc Department of Opthalmalogy Liaison, Health Program & Operations Novak, Mr. Sharon Faculty of Medicine Pretransfer Co-ordinator Section of Rehabilitation Medicine St. F etal:9 weeksto birth F irsteigh tweeksare furth er divided into 23 stages Stage one (day one) corresponds to fertiliz ation S ignificance • K nowledge ofdevelopmentofdifferentorgans,tissuesand systems. G rowth,differentiationand metabolism alloccurside by side inth e developingembryo. C om m onterm sused inem bryology • O ocyte (O vum)- amature secondary oocyte ready for fertiliz ation. C om m onterm sused inem bryology th • F etus-fetalperiod isfrom 9 week tillbirth wh ich is marked by differentiation,growth oftissuesand organsand subsequentweigh tgain. W ith more differentiationand growth,th e structure gradually ch angesto primary, secondary ordefinitive etc. G am etogenesis • Processofformationand developmentofspecializ ed generative cells– gamete • Preparessexcellsforfertiliz ation M eiosis • Producesh aploid gametes • A llowsrandom assortmentofmaternaland paternalch romosomesbetweenth e gametes • C rossingoverofch romosome segments-produces arecombinationofgeneticmaterial N ondisjunction-ch romosomally abnormalgametes • Inm ale th e sexorgansare th e testes wh ich produce sperm atoz oa(m ale gam etesorsperm s),44xy. S perm iogenesis • presence of prim ordialgerm cellsinth e sex cords(large pale cells). O ogenesisV sS perm atogenesis S im ilarities • P G C originate from th e sam e source and atth e sam e tim e. Secretory (progestational)-C h angesinfluenced by th e progesterone secretioninth e corpusluteum ofovary ( afterovulation). M enstruation Ifth ere isno fertiliz ation,progesterone secretionstopsafter14-15 days. Original and Review Articles – Original, and review articles are provided for residents who seek a more comprehensive understanding of a topic. We recognize that residency is a busy time, but we hope that you will take the time to read articles relevant to the management of your patients. In order to facilitate learning at many levels, several other educational opportunities are available. Tutorials – These are 20-30 minute sessions offered during the rotation that will provide the resident with hands on experience. The goal of morning rounds is to develop treatment plans that can be defended by the best available scientific evidence. In addition, morning rounds are an opportunity for residents to test their knowledge, gauge their progress in critical care education, and recognize the limits of the current medical practice. The faculty and fellows of Boston University Pulmonary and Critical Care section hope that you enjoy your rotation in the medical intensive care unit. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Ventilator-Associated Lung Injury / Literature D. Management and Optimal Timing of Tracheostomy / Literature Chapters on Cardiopulmonary Critical Care G. Treatment of Severe Sepsis & Shock: Part I (Fluids and Antibiotics) / Literature J.
Interneurons in the spinal cord connect the motor neuron of antagonist in such a way that activation of a muscle is automatically accompanied by deactivation of its antagonists cheap baclofen 25mg without a prescription muscle relaxant 10mg. Commands are sent out over efferent neurons and may stimulate or relax vascular smooth muscle proven baclofen 25 mg spasms while peeing, cause glandular secretion or alter intracellular metabolism buy 25mg baclofen mastercard spasms left shoulder blade. Endocrine Reflexes: Hormones as Chemical Messengers Hormones are the major types of chemical messengers in the body. There are two important aspects about the mechanism of hormonal information transfer. Hormone binds with the receptor - this complex causes changes in the specific activities of the target cell. Same hormone may increase secretion in one cell and cause contraction of the smooth muscle. Between these two extremes there is a range of cellular responses where the cell adapts to insult. These reactions include atrophy, hypoplasia, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, dysplasia and the accumulation within the cell of a variety of materials that may be endogenous (lipofuscin) or exogenous in origin. Atrophy presents as: loss of cell substance, shrinkage in cell size, cells have lowered functional ability, decrease in the number and size of its organelles, decrease in cell volume, and loss of more specific functions. Hypertrophy Stimulation of the parenchymal cells of an organ by increasing functional demand or by hormones, result in an increase in the total mass of the cells. This may be by hypertrophy such as in skeletal muscle or by an increase in number - hyperplasia. It is usually more common in cardiac and 53 skeletal muscle as in athletes and laborers in which individual muscle fibers increase in thickness and not in number. An increased oxygen availability to the working muscles Physiological Atrophy Physiologic atrophy is a normal phenomenon of aging in many tissues such as involution of thymus gland after adolescence, the reduction in endometrial cellularity after the menopause. Lack of hormonal stimulation causes the atrophic changes in the ovary, uterus, vagina, and fallopian tubes during menopause. Prostate, seminal vesicles, and bulbo-urelthral glands and the brain commonly atrophy in old age. In atrophy there is accumulation of Ripofuscin, a yellowish brown pigment inside the cytosol. Endocrine Atrophy In damage to the anterior pituitary gland there is diminution of the trophic hormone resulting in involution and atrophy of adrenal cortex and gonads. In endocrine hypofuncrion there may be significant atrophy of the hormone- dependent tissues e. Though synthetic activity lasts for sometime at a normal rate but catabolism is greatly enhanced. As the workload of a cell decreases, there is decline in oxygen consumption and protein synthesis and the cell conserves energy by decreasing the number and size of organelles. In general, reduced cell activity is associated with reduced catabolism, which in turn has a negative feedback. An anaphy is observed in the muscles of extremities that have been cast in plaster or weightlessness in case of astronauts. This leads to wasting of both muscles and bones; reversible with function recovery. Emaciation of starvation is mainly due to excessive utilization of the subcutaneous fat, but there is also wasting of lean mass muscles and even some organs such as liver. The term ‘cachexia’ means the combination of muscle wasting, organ shrinking, anemia and weakness, and is found in severely sick patients in whom there is loss of appetite, general gastrointestinal dysfunction associated with terminal stage of malignant tumor. The metabolic events of starvation permit life to continue for months without calorie intake, depending on the prestarvation stage. The daily weight loss, can range from one pound to several pounds on the stage of starvation. Protein loss ensues, with substantial weight loss, the most easily recognized sign of starvation. Biochemical changes that occur in starvation: • glycogenolysis (hepatic) continues for about 16 hours 56 • hepatic gluconeogenesis takes place using amino acids (especially muscle protein, there is increased urea excretion) • as brain and other tissues use ketone bodies, glucose need is reduced. Ketone bodies also reduce glucose use by muscles, gluconeogenesis, protein catabolism and urine concentration decreases • glutamine is used by the kidney for gluconeogenesis • Proteins are spared to permit maximal starvation; survival requires of at least ½ of muscle proteins. Other Types of Atrophies Increased catabolism in prolonged fever or as result of severe trauma may cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Tumors and cysts of an organ may cause pressure atrophy due to interference with blood flow or function of the tissue, e. Hypoplasia Hypoplasia is a state of failure of the tissue to reach normal size during development. The affected individuals have short limbs, trunk relatively normal length, the head large with bulging forehead and scooped out nose. In some type of dwarfism, the cause may be the reduced production of growth hormone as in Lorain type dwarfism in which growth hormone receptors are defective in some instances cell loss may be due to infection or poisoning. Maternal rubella infection in first trimester may damage the fetal heart and a variety of embryonic defects related to development arrest involving all germ layers. Delayed and disturbed organ genesis produces structural defects of eye, brain, heart, and large arteries. In hypoxic environment with low oxygen tension, there is compensatory hyperplasia of red cells precursors and increased number of circulating red blood cells is an example of compensatory hyperplasia. Hyperplasia is usually found in tissues that have the capability for mitosis, such as epidermis. An example of physiological hyperplasia is the enlargement of the breast in pregnancy in response to hormonal stimulation of target; an abnormal hormonal stimulation of target cell; an abnormally thick endometrium with excessive estrogen; such endometrium may bleed frequently. Metaplsia Metaplasia implies change of one cell type to another that allows the new cells to tolerate environmental stress. In metaplasia there is transformation of one type of differentiated tissue into another. In heavy smokers the surface epithelium of the bronchi changes from normal ciliated pseudo stratified columnar epithelium to stratified squamous. In this example chronic irritation or injury result in adaptive changes in the surface epithelium to a type resistant to smoke. What makes the internal environment, indicate some important variables, to be ` ` maintained within normal range? Elaborate reflex mechanism • autonomic reflex • somatic reflex • endocrine reflex 11. Nerve and muscle cells are excitable tissues developed a specialized use for the membrane potential. Action potentials are brief reversals of membrane potential brought about by rapid changes in membrane permeability. It means separation of electric charges across the membrane, or to a difference in the relative number of cations and anions in the intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid. It is primarily due to differences in the distribution and membrane permeability of sodium, potassium and large intracellular anions. All living cells have a slightly excess of positive charges outside and a corresponding slight excess of negative charges on the inside of its membrane.
Buy baclofen uk. 3-in-1 Foot and Leg Massager.